water (YMDB00890)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00890 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | water | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Water, also known as dihydrogen oxide or [OH2], belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. Water is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Water exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 7732-18-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 18.0153 Monoisotopic: 18.010564686 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/H2O/h1H2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | water | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | water | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | H2O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H]O[H] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 0 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
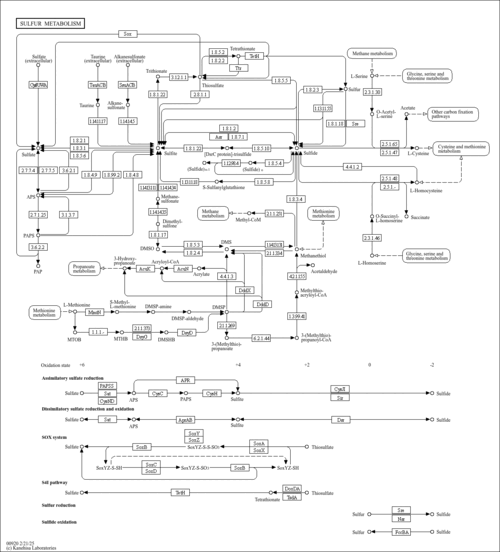
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in glutathione peroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- May constitute a glutathione peroxidase-like protective system against oxidative stresses
- Gene Name:
- GPX2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38143
- Molecular weight:
- 18406.0
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + H(2)O(2) → glutathione disulfide + 2 H(2)O. |
| 2 glutathione + a lipid hydroperoxide → glutathione disulfide + lipid + H2O |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Non-essential protein which is required for efficient N- glycosylation. Necessary for maintaining optimal levels of dolichol-linked oligosaccharides. Hydrolyzes dolichyl pyrophosphate at a very high rate and dolichyl monophosphate at a much lower rate. Does not act on phosphatidate
- Gene Name:
- CAX4
- Uniprot ID:
- P53223
- Molecular weight:
- 27648.80078
Reactions
| Dolichyl diphosphate + H(2)O → dolichyl phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate + 2- (formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ADE6
- Uniprot ID:
- P38972
- Molecular weight:
- 148904.0
Reactions
| ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O → ADP + phosphate + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- TRP3
- Uniprot ID:
- P00937
- Molecular weight:
- 53488.89844
Reactions
| Chorismate + L-glutamine → anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate. |
| 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate → 1-C-(3-indolyl)-glycerol 3-phosphate + CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxyl- or carbamoyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a "fusion" protein encoding three enzymatic activities of the pyrimidine pathway (GATase, CPSase, and ATCase)
- Gene Name:
- URA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07259
- Molecular weight:
- 245124.0
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O → 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
| Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate → phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Furnishes a means for formation of correctly charged Gln-tRNA(Gln) through the transamidation of misacylated Glu- tRNA(Gln) in the mitochondria. The reaction takes place in the presence of glutamine and ATP through an activated gamma-phospho- Glu-tRNA(Gln). Required for HMG2-induced ER-remodeling
- Gene Name:
- HER2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03557
- Molecular weight:
- 50918.0
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamyl-tRNA(Gln) + L-glutamine → ADP + phosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln) + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- CPA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P03965
- Molecular weight:
- 123914.0
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O → 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen
- Gene Name:
- URA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P28274
- Molecular weight:
- 64709.80078
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + xanthosine 5'-phosphate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + GMP + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- GUA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38625
- Molecular weight:
- 58481.80078
Reactions
| ATP + xanthosine 5'-phosphate + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + GMP + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ASN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P49089
- Molecular weight:
- 64469.60156
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ASN2
- Uniprot ID:
- P49090
- Molecular weight:
- 64592.5
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in amidophosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- 5-phospho-beta-D-ribosylamine + diphosphate + L-glutamate = L-glutamine + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ADE4
- Uniprot ID:
- P04046
- Molecular weight:
- 56718.89844
Reactions
| 5-phospho-beta-D-ribosylamine + diphosphate + L-glutamate → L-glutamine + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen. Plays an important role in the regulation of phospholipid synthesis
- Gene Name:
- URA8
- Uniprot ID:
- P38627
- Molecular weight:
- 63055.69922
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + deamido-NAD(+) + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + NAD(+) + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- QNS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38795
- Molecular weight:
- 80684.89844
Reactions
| ATP + deamido-NAD(+) + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + NAD(+) + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of urea to ammonia and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- DUR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32528
- Molecular weight:
- 201830.0
Reactions
| ATP + urea + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + urea-1-carboxylate. |
| Urea-1-carboxylate + H(2)O → 2 CO(2) + 2 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in allantoicase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P25335
- Molecular weight:
- 38713.5
Reactions
| Allantoate + H(2)O → (S)-ureidoglycolate + urea. |
- General function:
- Involved in arginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-arginine + H(2)O = L-ornithine + urea
- Gene Name:
- CAR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00812
- Molecular weight:
- 35661.60156
Reactions
| L-arginine + H(2)O → L-ornithine + urea. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O = 2 D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- NTH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P35172
- Molecular weight:
- 89678.60156
Reactions
| Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O → 2 D-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O = 2 D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- ATH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P48016
- Molecular weight:
- 136919.0
Reactions
| Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O → 2 D-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O = 2 D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- NTH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32356
- Molecular weight:
- 85878.5
Reactions
| Alpha,alpha-trehalose + H(2)O → 2 D-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphatase catalytic subunit of the trehalose synthase complex that catalyzes the production of trehalose from glucose-6- phosphate and UDP-glucose in a two step process
- Gene Name:
- TPS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P31688
- Molecular weight:
- 102976.0
Reactions
| Trehalose 6-phosphate + H(2)O → trehalose + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the irreversible transamination of the L- tryptophan metabolite L-kynurenine to form kynurenic acid (KA)
- Gene Name:
- BNA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P47039
- Molecular weight:
- 50081.89844
Reactions
| L-kynurenine + 2-oxoglutarate → 4-(2-aminophenyl)-2,4-dioxobutanoate + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- This is predominantly if not solely a fructose-2,6- bisphosphatase
- Gene Name:
- FBP26
- Uniprot ID:
- P32604
- Molecular weight:
- 52594.5
Reactions
| Beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate + H(2)O → D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Synthesis and degradation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06137
- Molecular weight:
- 58385.19922
Reactions
| Beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate + H(2)O → D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate. |
| ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate → ADP + beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- May eliminate potentially toxic dinucleoside polyphosphates during sporulation. Most active against diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P6-hexaphosphate (Ap6A). Can also hydrolyze diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P5-pentaphosphate (Ap5A), adenosine 5'-pentaphosphate, and adenosine 5'-tetraphosphate are also substrates, but not diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) or other dinucleotides, mononucleotides, nucleotide sugars, or nucleotide alcohols. Also cleaves a beta-phosphate from the diphosphate groups in PP-InsP5 (diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate) and [PP]2-InsP4 (bisdiphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate)
- Gene Name:
- DDP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99321
- Molecular weight:
- 21572.30078
Reactions
| Diphospho-myo-inositol polyphosphate + H(2)O → myo-inositol polyphosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in inositol trisphosphate 3-kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) to diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (InsP7/PP-InsP5). Involved in phosphate regulation and polyphosphate accumulation. Required for resistance to salt stress, cell wall integrity, vacuole morphogenesis, and telomere maintenance
- Gene Name:
- KCS1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12494
- Molecular weight:
- 119549.0
Reactions
| ATP + 1D-myo-inositol hexakisphosphate → ADP + 5-diphospho-1D-myo-inositol (1,2,3,4,6)pentakisphosphate. |
| ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate → ADP + diphospho-1D-myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate (isomeric configuration unknown). |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional inositol kinase that catalyzes the formation of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (InsP7 or PP- InsP5) and bi-diphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate (InsP8 or PP2- InsP4). Converts inositolitol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) to InsP7. Also able to convert InsP7 to InsP8. Probably specifically mediates the formation of 4PP-InsP5 and 6PP-InsP5 InsP7 isomers but not of 5PP-IP5 InsP7 isomer. Required for maintaining celllular integrity, normal growth and interactions with the ARP complex. Acts as a regulator of the PHO80-PHO85 cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complex, thereby regulating signaling of phosphate availability. Required for the function of the cortical actin cytoskeleton, possibly by participating in correct F-actin localization and ensuring polarized growth
- Gene Name:
- VIP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06685
- Molecular weight:
- 129754.0
Reactions
| ATP + 1D-myo-inositol hexakisphosphate → ADP + 5-diphospho-1D-myo-inositol (1,2,3,4,6)pentakisphosphate. |
| ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate → ADP + diphospho-1D-myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate (isomeric configuration unknown). |
| ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 5-diphosphate pentakisphosphate → ADP + 1D-myo-inositol bisdiphosphate tetrakisphosphate (isomeric configuration unknown). |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes C14-demethylation of lanosterol which is critical for ergosterol biosynthesis. It transforms lanosterol into 4,4'-dimethyl cholesta-8,14,24-triene-3-beta-ol
- Gene Name:
- ERG11
- Uniprot ID:
- P10614
- Molecular weight:
- 60719.80078
Reactions
| Obtusifoliol + 3 O(2) + 3 NADPH → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-ergosta-8,14,24(28)-trien-3-beta-ol + formate + 3 NADP(+) + 4 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Interconversion of serine and glycine
- Gene Name:
- SHM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P37291
- Molecular weight:
- 52218.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + glycine + H(2)O → tetrahydrofolate + L-serine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Interconversion of serine and glycine
- Gene Name:
- SHM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P37292
- Molecular weight:
- 53686.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + glycine + H(2)O → tetrahydrofolate + L-serine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(+)-dependent cleavage of saccharopine to L-lysine and 2-oxoglutarate
- Gene Name:
- LYS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38998
- Molecular weight:
- 41464.39844
Reactions
| N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NAD(+) + H(2)O → L-lysine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NADP(+) + H(2)O = L-glutamate + L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- LYS9
- Uniprot ID:
- P38999
- Molecular weight:
- 48917.30078
Reactions
| N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NADP(+) + H(2)O → L-glutamate + L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- ALD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P47771
- Molecular weight:
- 55187.39844
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NADH
- Gene Name:
- ALD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P46367
- Molecular weight:
- 56723.19922
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- ALD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54114
- Molecular weight:
- 55384.80078
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NADH
- Gene Name:
- ALD6
- Uniprot ID:
- P54115
- Molecular weight:
- 54413.69922
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Minor mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase isoform. Plays a role in regulation or biosynthesis of electron transport chain components. Involved in the biosynthesis of acetate during anaerobic growth on glucose
- Gene Name:
- ALD5
- Uniprot ID:
- P40047
- Molecular weight:
- 56620.39844
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
| An aldehyde + NADP(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the enolization of 2,3-diketo-5-methylthiopentyl-1-phosphate (DK-MTP-1-P) into the intermediate 2-hydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentenyl-1-phosphate (HK-MTPenyl-1-P), which is then dephosphorylated to form the acireductone 1,2-dihydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentene (DHK-MTPene)
- Gene Name:
- UTR4
- Uniprot ID:
- P32626
- Molecular weight:
- 25187.19922
Reactions
| 5-(methylthio)-2,3-dioxopentyl phosphate + H(2)O → 1,2-dihydroxy-5-(methylthio)pent-1-en-3-one + phosphate. |
| 2-Phosphoglycolate + H2O → glycolate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dehydration of methylthioribulose-1- phosphate (MTRu-1-P) into 2,3-diketo-5-methylthiopentyl-1- phosphate (DK-MTP-1-P)
- Gene Name:
- MDE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P47095
- Molecular weight:
- 27426.59961
Reactions
| S-methyl-5-thio-D-ribulose 1-phosphate → 5-(methylthio)-2,3-dioxopentyl phosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Required for growth on nonfermentable carbon sources and for biosynthesis of glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ACO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P19414
- Molecular weight:
- 85367.5
Reactions
| Citrate → isocitrate. |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydroorotase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- URA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P20051
- Molecular weight:
- 40313.0
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O → N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- The AROM polypeptide catalyzes 5 consecutive enzymatic reactions in prechorismate polyaromatic amino acid biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- ARO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08566
- Molecular weight:
- 174754.0
Reactions
| 3-deoxy-D-arabino-hept-2-ulosonate 7-phosphate → 3-dehydroquinate + phosphate. |
| 3-dehydroquinate → 3-dehydroshikimate + H(2)O. |
| Shikimate + NADP(+) → 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH. |
| ATP + shikimate → ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + 3-phosphoshikimate → phosphate + 5-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-3-phosphoshikimate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Stereospecific condensation of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and D-erythrose-4-phosphate (E4P) giving rise to 3-deoxy-D- arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP)
- Gene Name:
- ARO4
- Uniprot ID:
- P32449
- Molecular weight:
- 39748.80078
Reactions
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + D-erythrose 4-phosphate + H(2)O → 3-deoxy-D-arabino-hept-2-ulosonate 7-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Stereospecific condensation of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and D-erythrose-4-phosphate (E4P) giving rise to 3-deoxy-D- arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP)
- Gene Name:
- ARO3
- Uniprot ID:
- P14843
- Molecular weight:
- 41069.5
Reactions
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + D-erythrose 4-phosphate + H(2)O → 3-deoxy-D-arabino-hept-2-ulosonate 7-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ureidoglycolate hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32459
- Molecular weight:
- 21726.59961
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + H(2)O → glyoxylate + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- This isozyme is necessary for growth on acetate as sole C-source
- Gene Name:
- MLS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P30952
- Molecular weight:
- 62790.60156
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate → (S)-malate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- This isozyme is involved in the degradation of allantoin (purine catabolism)
- Gene Name:
- DAL7
- Uniprot ID:
- P21826
- Molecular weight:
- 62793.39844
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate → (S)-malate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxamine-phosphate oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of either pyridoxine 5'- phosphate (PNP) or pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP) into pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)
- Gene Name:
- PDX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38075
- Molecular weight:
- 26908.0
Reactions
| Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate + H(2)O + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
| Pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in peptidyl-lysine modification to hypusine
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent oxidative cleavage of spermidine and the subsequent transfer of the butylamine moiety of spermidine to the epsilon-amino group of a specific lysine residue of the eIF-5A precursor protein to form the intermediate deoxyhypusine residue
- Gene Name:
- DYS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38791
- Molecular weight:
- 42891.80078
Reactions
| [eIF5A-precursor]-lysine + spermidine → [eIF5A-precursor]-deoxyhypusine + propane-1,3-diamine. |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the production of beta-alanine, a precursor of pantothenic acid. Multicopy suppressor of fenpropimorph resistance
- Gene Name:
- FMS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P50264
- Molecular weight:
- 57805.10156
Reactions
| Spermine + O(2) + H(2)O → spermidine + 3-aminopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| Spermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → putrescine + 3-aminopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(1)-acetylspermine + O(2) + H(2)O → spermidine + 3-acetamidopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(1)-acetylspermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → putrescine + 3-acetamidopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(8)-acetylspermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → 4-acetamidobutanal + trimethylenediamine + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + 2-oxoglutarate = (R)-2- hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- LYS21
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12122
- Molecular weight:
- 48593.80078
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + 2-oxoglutarate → (R)-2-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-isopropylmalate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA with 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate (2-oxoisovalerate) to form 3-carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate (2-isopropylmalate). Redundant to LEU4, responsible of about 20% of alpha-IPMS activity. Involved in leucine synthesis
- Gene Name:
- LEU9
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12166
- Molecular weight:
- 67199.60156
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H(2)O → (2S)-2-isopropylmalate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in synthesis of 1,3-beta-glucan. Could be a subunit of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase. Could be also a component of the membrane bound fatty acid elongation systems that produce the 26-carbon very long chain fatty acids that are precursors for ceramide and sphingolipids. Appears to be involved in the elongation of fatty acids up to 24 carbons. Appears to have the highest affinity for substrates with chain length less than 22 carbons
- Gene Name:
- FEN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25358
- Molecular weight:
- 40001.80078
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA (HIBYL-CoA), a saline catabolite. Has high activity toward isobutyryl-CoA. Could be an isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase that functions in valine catabolism. Also hydrolyzes 3-hydroxypropanoyl-CoA. Has an indirect role in endocytic membrane trafficking. May have a function in protein biosynthesis in mitochondrial small ribosomal subunit
- Gene Name:
- EHD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28817
- Molecular weight:
- 56287.89844
Reactions
| 3-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoyl-CoA + H(2)O → CoA + 3-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Presumably involved in regulating the intracellular acetyl-CoA pool for fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis and fatty acid oxidation. It may be involved in overall regulation of acetylation during melatonin synthesis
- Gene Name:
- ACH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32316
- Molecular weight:
- 58711.5
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O → CoA + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-CoA + O(2) = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2)
- Gene Name:
- POX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13711
- Molecular weight:
- 84041.39844
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + O(2) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme condenses acetyl-CoA with acetoacetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA, which is the substrate for HMG-CoA reductase
- Gene Name:
- ERG13
- Uniprot ID:
- P54839
- Molecular weight:
- 55013.10156
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + acetoacetyl-CoA → (S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-isopropylmalate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA with 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate (2-oxoisovalerate) to form 3-carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate (2-isopropylmalate)
- Gene Name:
- LEU4
- Uniprot ID:
- P06208
- Molecular weight:
- 68408.29688
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H(2)O → (2S)-2-isopropylmalate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- May be a membrane bound enzyme involved in the highly specific elongation of saturated 14-carbon fatty acids (14:0) to 16-carbon species (16:0)
- Gene Name:
- ELO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39540
- Molecular weight:
- 36233.60156
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Carrier of the growing fatty acid chain in fatty acid biosynthesis. May be involved in the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids. Accessory and non-catalytic subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), which functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain
- Gene Name:
- ACP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32463
- Molecular weight:
- 13942.5
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + 2-oxoglutarate = (R)-2- hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- LYS20
- Uniprot ID:
- P48570
- Molecular weight:
- 47098.39844
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + 2-oxoglutarate → (R)-2-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in acyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Acyltransferase which mediates the conversion of 1-acyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (LPC) into phosphatidylcholine (PC). Displays a broad LPC fatty acyl chain substrate specificity utilizing LPC molecules ranging in length from C-10 to C-20. Does not utilize other lysolipids than LPC as acceptor. Also shows acyl-CoA-independent acyltransferase activity. Required for normal phospholipid content of mitochondrial membranes. Involved in the remodeling of the acyl groups of cardiolipin in the mitochondrial inner membrane, which affects the assembly and stability of respiratory chain complex IV and its supercomplex forms
- Gene Name:
- TAZ1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06510
- Molecular weight:
- 44187.19922
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine → CoA + 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Acyl-CoA + acetyl-CoA = CoA + 3-oxoacyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- POT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P27796
- Molecular weight:
- 44729.89844
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + acetyl-CoA → CoA + 3-oxoacyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long- chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. The beta subunit contains domains for:[acyl-carrier-protein] acetyltransferase and malonyltransferase, S-acyl fatty acid synthase thioesterase, enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase, and 3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase
- Gene Name:
- FAS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07149
- Molecular weight:
- 228689.0
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADH + 2n NADPH → long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO(2) + 2n NAD(+) + 2n NADP(+). |
| Acetyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + acetyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| Malonyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| (3R)-3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → hexadec-2-enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O. |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH. |
| Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O → [acyl-carrier-protein] + oleate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- CIT3
- Uniprot ID:
- P43635
- Molecular weight:
- 53810.69922
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate → citrate + CoA. |
| propanoyl-CoA + H2O + oxaloacetate → (2R,3S)-2-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate + CoA |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Transfers the 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety from coenzyme A to a Ser of mitochondrial acyl-carrier-protein
- Gene Name:
- PPT2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12036
- Molecular weight:
- 19973.0
Reactions
| CoA-(4'-phosphopantetheine) + apo-[acyl-carrier-protein] → adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + holo-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA thioesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-CoA thioesterases are a group of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A (CoASH), providing the potential to regulate intracellular levels of acyl-CoAs, free fatty acids and CoASH
- Gene Name:
- TES1
- Uniprot ID:
- P41903
- Molecular weight:
- 40259.39844
Reactions
| Palmitoyl-CoA + H(2)O → CoA + palmitate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- CIT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P08679
- Molecular weight:
- 51412.89844
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate → citrate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- CIT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00890
- Molecular weight:
- 53359.60156
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate → citrate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine = L- cystathionine + succinate
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04533
- Molecular weight:
- 74312.70313
Reactions
| O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine → L-cystathionine + succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate
- Gene Name:
- CYS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P31373
- Molecular weight:
- 42541.69922
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Mediates extracellular nucleotide derived phosphate hydrolysis along with NPP2 and PHO5
- Gene Name:
- NPP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25353
- Molecular weight:
- 84733.20313
Reactions
| A dinucleotide + H(2)O → 2 mononucleotides. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphoanhydride bonds of nucleoside tri- and di-phosphates. Has equal high activity toward ADP/ATP, GDP/GTP, and UDP/UTP and approximately 50% less toward CDP/CTP and thiamine pyrophosphate. Has no activity toward GMP. Required for Golgi glycosylation and cell wall integrity. Together with CDC55, required for adenovirus E4orf4 (early region 4 open reading frame 4) induced toxicity, the apyrase activity is not required for this function. Plays a role in sphingolipid synthesis
- Gene Name:
- YND1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40009
- Molecular weight:
- 71851.20313
Reactions
| ATP + 2 H(2)O → AMP + 2 phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Mediates extracellular nucleotide derived phosphate hydrolysis along with NPP1 and PHO5
- Gene Name:
- NPP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P39997
- Molecular weight:
- 57354.10156
Reactions
| A dinucleotide + H(2)O → 2 mononucleotides. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Could be an enzyme that inactivates 6-azauracil by modifying it
- Gene Name:
- SDT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53078
- Molecular weight:
- 31968.40039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- This enzyme scavenge exogenous and endogenous cytidine and 2'-deoxycytidine for UMP synthesis
- Gene Name:
- CDD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06549
- Molecular weight:
- 15535.90039
Reactions
| Cytidine + H(2)O → uridine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes the N-acetamido groups of N-acetyl-D- glucosamine residues in chitin
- Gene Name:
- CDA1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06702
- Molecular weight:
- 34642.0
Reactions
| Chitin + H(2)O → chitosan + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes the N-acetamido groups of N-acetyl-D- glucosamine residues in chitin
- Gene Name:
- CDA2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06703
- Molecular weight:
- 35692.80078
Reactions
| Chitin + H(2)O → chitosan + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-acetylglucosaminylphosphatidylinositol de
- Specific function:
- Involved in the second step of GPI biosynthesis. De-N- acetylation of N-acetylglucosaminyl-phosphatidylinositol
- Gene Name:
- GPI12
- Uniprot ID:
- P23797
- Molecular weight:
- 35445.60156
Reactions
| 6-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol + H(2)O → 6-(alpha-D-glucosaminyl)-1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutathione peroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- May constitute a glutathione peroxidase-like protective system against oxidative stresses
- Gene Name:
- GPX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36014
- Molecular weight:
- 19484.5
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + H(2)O(2) → glutathione disulfide + 2 H(2)O. |
| 2 glutathione + a lipid hydroperoxide → glutathione disulfide + lipid + H2O |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- AAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53909
- Molecular weight:
- 39634.69922
Reactions
| Adenosine + H(2)O → inosine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in adenosylhomocysteinase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosylhomocysteine is a competitive inhibitor of S- adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyl transferase reactions; therefore adenosylhomocysteinase may play a key role in the control of methylations via regulation of the intracellular concentration of adenosylhomocysteine
- Gene Name:
- SAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39954
- Molecular weight:
- 49125.10156
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + adenosine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. RNR2 provides the diiron-tyrosyl radical center
- Gene Name:
- RNR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P09938
- Molecular weight:
- 46147.0
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides
- Gene Name:
- RNR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21524
- Molecular weight:
- 99560.20313
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4- carboxylate = 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ADE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P21264
- Molecular weight:
- 62338.69922
Reactions
| 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate → 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- D-erythro-1-(imidazol-4-yl)glycerol 3- phosphate = 3-(imidazol-4-yl)-2-oxopropyl phosphate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- HIS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P06633
- Molecular weight:
- 23833.0
Reactions
| D-erythro-1-(imidazol-4-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate → 3-(imidazol-4-yl)-2-oxopropyl phosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- CHA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25379
- Molecular weight:
- 39301.0
Reactions
| L-serine → pyruvate + NH(3). |
| L-threonine → 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Glycerophosphocholine glycerophosphodiesterase responsible for the hydrolysis of intracellular glycerophosphocholine into glycerol-phosphate and choline. The choline is used for phosphatidyl-choline synthesis. Required for utilization of glycerophosphocholine as phosphate source
- Gene Name:
- GDE1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02979
- Molecular weight:
- 138013.0
Reactions
| A glycerophosphodiester + H(2)O → an alcohol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Glycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O = glycerol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- HOR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P40106
- Molecular weight:
- 27813.5
Reactions
| Glycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O → glycerol + phosphate. |
| glycerol 1-phosphate + H2O → glycerol + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Probable glycerophosphocholine glycerophosphodiesterase which may be responsible for the hydrolysis of intracellular glycerophosphocholine into glycerol-phosphate and choline. The choline is used for phosphatidyl-choline synthesis
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08959
- Molecular weight:
- 37069.39844
Reactions
| A glycerophosphodiester + H(2)O → an alcohol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Glycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O = glycerol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- RHR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P41277
- Molecular weight:
- 27946.59961
Reactions
| Glycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O → glycerol + phosphate. |
| glycerol 1-phosphate + H2O → glycerol + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in oxygen-dependent protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen-IX to form protoporphyrin-IX
- Gene Name:
- HEM14
- Uniprot ID:
- P40012
- Molecular weight:
- 59702.39844
Reactions
| Protoporphyrinogen-IX + 3 O(2) → protoporphyrin-IX + 3 H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoric ester hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H(2)O = D- fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- FBP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09201
- Molecular weight:
- 38262.19922
Reactions
| D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H(2)O → D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase activity
- Specific function:
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- MIS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09440
- Molecular weight:
- 106216.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) → 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH. |
| 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O → 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
| ATP + formate + tetrahydrofolate → ADP + phosphate + 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in IMP cyclohydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + 5-amino-1-(5- phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide = tetrahydrofolate + 5- formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide
- Gene Name:
- ADE17
- Uniprot ID:
- P38009
- Molecular weight:
- 65262.60156
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide → tetrahydrofolate + 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
| IMP + H(2)O → 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in IMP cyclohydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + 5-amino-1-(5- phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide = tetrahydrofolate + 5- formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide
- Gene Name:
- ADE16
- Uniprot ID:
- P54113
- Molecular weight:
- 65281.80078
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide → tetrahydrofolate + 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
| IMP + H(2)O → 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Formylates methionyl-tRNA in mitochondria
- Gene Name:
- FMT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32785
- Molecular weight:
- 44616.19922
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + L-methionyl-tRNA(fMet) + H(2)O → tetrahydrofolate + N-formylmethionyl-tRNA(fMet). |
- General function:
- Involved in formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase activity
- Specific function:
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ADE3
- Uniprot ID:
- P07245
- Molecular weight:
- 102204.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) → 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH. |
| 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O → 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
| ATP + formate + tetrahydrofolate → ADP + phosphate + 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in porphobilinogen synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen
- Gene Name:
- HEM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P05373
- Molecular weight:
- 37739.69922
Reactions
| 2 5-aminolevulinate → porphobilinogen + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in heme biosynthesis. Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of propionic acid side chains of rings A and B of coproporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- HEM13
- Uniprot ID:
- P11353
- Molecular weight:
- 37711.30078
Reactions
| Coproporphyrinogen-III + O(2) + 2 H(+) → protoporphyrinogen-IX + 2 CO(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Could be a fumarate reductase
- Gene Name:
- OSM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21375
- Molecular weight:
- 55064.80078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- PHO11
- Uniprot ID:
- P35842
- Molecular weight:
- 52757.39844
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Partially mediates extracellular nucleotide derived phosphate hydrolysis along with NPP1 and NPP2
- Gene Name:
- PHO5
- Uniprot ID:
- P00635
- Molecular weight:
- 52858.10156
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts cytosine to uracil or 5-methylcytosine to thymine by deaminating carbon number 4
- Gene Name:
- FCY1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12178
- Molecular weight:
- 17506.90039
Reactions
| Cytosine + H(2)O → uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the deamidation of nicotinamide, an early step in the NAD(+) salvage pathway. Positively regulates SIR2-mediated silencing and longevity by preventing the accumulation of intracellular nicotinamide, an inhibitor of SIR2, during times of stress. Acts also on nicotinyl hydroxamate
- Gene Name:
- PNC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53184
- Molecular weight:
- 24993.19922
Reactions
| Nicotinamide + H(2)O → nicotinate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- GDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P33327
- Molecular weight:
- 124331.0
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP3-1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11163
- Molecular weight:
- 38686.19922
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH3
- Uniprot ID:
- P39708
- Molecular weight:
- 49626.80078
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylbilane synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Tetrapolymerization of the monopyrrole PBG into the hydroxymethylbilane pre-uroporphyrinogen in several discrete steps
- Gene Name:
- HEM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28789
- Molecular weight:
- 36674.19922
Reactions
| 4 porphobilinogen + H(2)O → hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex) catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- GCV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P48015
- Molecular weight:
- 44468.69922
Reactions
| [Protein]-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + tetrahydrofolate → [protein]-dihydrolipoyllysine + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38986
- Molecular weight:
- 41394.80078
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07262
- Molecular weight:
- 49569.60156
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Exhibits dehydratase activity specific for L-threo-3- hydroxyaspartate
- Gene Name:
- SRY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36007
- Molecular weight:
- 34898.69922
Reactions
| Threo-3-hydroxy-L-aspartate → oxaloacetate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- STR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53101
- Molecular weight:
- 51828.0
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- AMP deaminase plays a critical role in energy metabolism
- Gene Name:
- AMD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15274
- Molecular weight:
- 93300.79688
Reactions
| AMP + H(2)O → IMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in riboflavin biosynthesis. Converts 2,5- diamino-6-(ribosylamino)-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate into 5- amino-6-(ribosylamino)-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione 5'-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- RIB2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12362
- Molecular weight:
- 67035.29688
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
| 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine + H(2)O → 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- IRC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P43623
- Molecular weight:
- 36971.10156
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Supplies the nucleotide substrate for thymidylate synthetase
- Gene Name:
- DCD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06773
- Molecular weight:
- 35645.69922
Reactions
| dCMP + H(2)O → dUMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of guanine, producing xanthine and ammonia
- Gene Name:
- GUD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07729
- Molecular weight:
- 55203.19922
Reactions
| Guanine + H(2)O → xanthine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate hydroxymethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + 3-methyl-2- oxobutanoate + H(2)O = tetrahydrofolate + 2-dehydropantoate
- Gene Name:
- ECM31
- Uniprot ID:
- P38122
- Molecular weight:
- 34464.69922
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H(2)O → tetrahydrofolate + 2-dehydropantoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3'(2'),5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) to adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) and 3'(2')-phosphoadenosine 5'- phosphate (PAP) to AMP. Regulates the flux of sulfur in the sulfur-activation pathway by converting PAPS to APS. Involved in salt tolerance. Confers resistance to lithium
- Gene Name:
- HAL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P32179
- Molecular weight:
- 39148.89844
Reactions
| Adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + H(2)O → adenosine 5'-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- NAD(+) + H(2)O = AMP + NMN
- Gene Name:
- NPY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53164
- Molecular weight:
- 43516.0
Reactions
| NAD(+) + H(2)O → AMP + NMN. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls the level of cAMP in yeast cells, together with the high-affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE2)
- Gene Name:
- PDE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22434
- Molecular weight:
- 42015.69922
Reactions
| Nucleoside 3',5'-cyclic phosphate + H(2)O → nucleoside 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Cleaves A-5'-PPP-5'A to yield AMP and ADP. Can cleave all dinucleoside polyphosphates, provided the phosphate chain contains at least 3 phosphates and that 1 of the 2 bases composing the nucleotide is a purine. Is most effective on dinucleoside triphosphates. Negatively regulates intracellular dinucleoside polyphosphate levels, which elevate following heat shock
- Gene Name:
- HNT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P49775
- Molecular weight:
- 23541.59961
Reactions
| P(1)-P(3)-bis(5'-adenosyl) triphosphate + H(2)O → ADP + AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- ADP-ribose + H(2)O = AMP + D-ribose 5- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- YSA1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01976
- Molecular weight:
- 26086.80078
Reactions
| ADP-ribose + H(2)O → AMP + D-ribose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the activation of alpha-aminoadipate by ATP- dependent adenylation and the reduction of activated alpha- aminoadipate by NADPH
- Gene Name:
- LYS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07702
- Molecular weight:
- 155344.0
Reactions
| L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → L-2-aminoadipate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Controls the level of cAMP in yeast cells, together with the low-affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE1)
- Gene Name:
- PDE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P06776
- Molecular weight:
- 60999.19922
Reactions
| Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate + H(2)O → adenosine 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Formation of pseudouridine at positions 27 and 28 in the anticodon stem and loop of transfer RNAs; at positions 34 and 36 of intron-containing precursor tRNA(Ile) and at position 35 in the intron-containing tRNA(Tyr)
- Gene Name:
- PUS1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12211
- Molecular weight:
- 62142.0
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA processing
- Specific function:
- Responsible for synthesis of pseudouridine from uracil- 55 in the psi GC loop of transfer RNAs
- Gene Name:
- PUS4
- Uniprot ID:
- P48567
- Molecular weight:
- 45273.10156
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Formation of pseudouridine in the anticodon stem and loop of transfer RNAs
- Gene Name:
- PUS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P53167
- Molecular weight:
- 41874.80078
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Formation of pseudouridines at positions 38 and 39 in the anticodon stem and loop of transfer RNAs
- Gene Name:
- PUS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P31115
- Molecular weight:
- 50888.30078
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
- General function:
- Involved in fumarate hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- FUM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08417
- Molecular weight:
- 53151.5
Reactions
| (S)-malate → fumarate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in monooxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) to form 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine (L-3OHKyn). Required for synthesis of quinolinic acid
- Gene Name:
- BNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P38169
- Molecular weight:
- 52428.89844
Reactions
| L-kynurenine + NADPH + O(2) → 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine + NADP(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) and L-3- hydroxykynurenine (L-3OHKyn) into anthranilic acid (AA) and 3- hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-OHAA), respectively
- Gene Name:
- BNA5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05979
- Molecular weight:
- 51031.60156
Reactions
| L-kynurenine + H(2)O → anthranilate + L-alanine. |
| L-3-hydroxykynurenine + H(2)O → 3-hydroxyanthranilate + L-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-isopropylmalate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the isomerization between 2-isopropylmalate and 3-isopropylmalate, via the formation of 2-isopropylmaleate
- Gene Name:
- LEU1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07264
- Molecular weight:
- 85793.70313
Reactions
| (2R,3S)-3-isopropylmalate → (2S)-2-isopropylmaleate + H(2)O. |
| (2S)-2-isopropylmaleate + H(2)O → (2S)-2-isopropylmalate. |
- General function:
- Involved in methionine adenosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of S-adenosylmethionine from methionine and ATP
- Gene Name:
- SAM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P10659
- Molecular weight:
- 41818.0
Reactions
| ATP + L-methionine + H(2)O → phosphate + diphosphate + S-adenosyl-L-methionine. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) to HMP-PP, and also probaby that of HMP to HMP- P
- Gene Name:
- THI20
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08224
- Molecular weight:
- 61268.89844
Reactions
| ATP + 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine → ADP + 4-amino-5-phosphonooxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine. |
| ATP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-phosphomethylpyrimidine → ADP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-diphosphomethylpyrimidine. |
| thiamine + H2O → 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine + 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- The plasma membrane ATPase of plants and fungi is a hydrogen ion pump. The proton gradient it generates drives the active transport of nutrients by H(+)-symport. The resulting external acidification and/or internal alkinization may mediate growth responses
- Gene Name:
- PMA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05030
- Molecular weight:
- 99618.39844
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- PHO8
- Uniprot ID:
- P11491
- Molecular weight:
- 63003.60156
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
| (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + H(2)O → (2E,6E)-farnesol + diphosphate. |
| beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate + H2O → beta-D-fructofuranose 2-phosphate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- The plasma membrane ATPase of plants and fungi is a hydrogen ion pump. The proton gradient it generates drives the active transport of nutrients by H(+)-symport. The resulting external acidification and/or internal alkinization may mediate growth responses
- Gene Name:
- PMA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P19657
- Molecular weight:
- 102171.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Subunits alpha and beta form the catalytic core in F(1). Rotation of the central stalk against the surrounding alpha(3)beta(3) subunits leads to hydrolysis of ATP in three separate catalytic sites on the beta subunits
- Gene Name:
- ATP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P00830
- Molecular weight:
- 54793.30078
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- TDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00360
- Molecular weight:
- 35749.60156
Reactions
| D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) → 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The outer membrane form may mediate the reduction of outer membrane cytochrome b5, and the soluble inter-membrane space form may transfer electrons from external NADH to cytochrome c, thereby mediating an antimycin-insensitive, energy-coupled oxidation of external NADH by yeast mitochondria. Involved in the reduction of D-erythroascorbyl free radicals
- Gene Name:
- MCR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36060
- Molecular weight:
- 34137.69922
Reactions
| NADH + 2 ferricytochrome b5 → NAD(+) + H(+) + 2 ferrocytochrome b5. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-AMP + H(2)O = 1-(5- phosphoribosyl)-5-((5- phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide
- Gene Name:
- HIS4
- Uniprot ID:
- P00815
- Molecular weight:
- 87720.5
Reactions
| 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-AMP + H(2)O → 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-((5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
| 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-ATP + H(2)O → 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-AMP + diphosphate. |
| L-histidinol + H(2)O + 2 NAD(+) → L-histidine + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Second trifunctional enzyme acting on the beta-oxidation pathway for fatty acids, possessing hydratase-dehydrogenase- epimerase activities. Converts trans-2-enoyl-CoA via D-3- hydroxyacyl-CoA to 3-ketoacyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- FOX2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02207
- Molecular weight:
- 98702.39844
Reactions
| (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA → (2E)-2-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- IMD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P50095
- Molecular weight:
- 56584.39844
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O → xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- IMD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38697
- Molecular weight:
- 56529.5
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O → xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- IMD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39567
- Molecular weight:
- 44385.80078
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O → xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- O-phospho-L(or D)-serine + H(2)O = L(or D)- serine + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- SER2
- Uniprot ID:
- P42941
- Molecular weight:
- 34207.0
Reactions
| O-phospho-L(or D)-serine + H(2)O → L(or D)-serine + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine biosynthetic process from serine
- Specific function:
- L-serine + L-homocysteine = L-cystathionine + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- CYS4
- Uniprot ID:
- P32582
- Molecular weight:
- 56021.30078
Reactions
| L-serine + L-homocysteine → L-cystathionine + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-serine + 1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3- phosphate = L-tryptophan + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- TRP5
- Uniprot ID:
- P00931
- Molecular weight:
- 76625.5
Reactions
| L-serine + 1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate → L-tryptophan + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of sulfite to sulfide, one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L-cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- ECM17
- Uniprot ID:
- P47169
- Molecular weight:
- 161218.0
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O → sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L-cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- MET10
- Uniprot ID:
- P39692
- Molecular weight:
- 114827.0
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O → sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in histidinol-phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- L-histidinol phosphate + H(2)O = L-histidinol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- HIS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38635
- Molecular weight:
- 38581.5
Reactions
| L-histidinol phosphate + H(2)O → L-histidinol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 6-phosphogluconolactonase activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6- phosphogluconate
- Gene Name:
- SOL4
- Uniprot ID:
- P53315
- Molecular weight:
- 28447.5
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + H(2)O → 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 6-phosphogluconolactonase activity
- Specific function:
- May be involved in regulation of tRNA subcellular distribution
- Gene Name:
- SOL1
- Uniprot ID:
- P50278
- Molecular weight:
- 35652.19922
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in 6-phosphogluconolactonase activity
- Specific function:
- May be involved in regulation of tRNA subcellular distribution
- Gene Name:
- SOL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P37262
- Molecular weight:
- 34500.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in protein complex assembly
- Specific function:
- Required for the assembly of yeast cytochrome oxidase. Involved in the biosynthesis of heme A and the initial step in this pathway, the hydroxylation of heme O, is thought to be catalyzed by a three-component mono-oxygenase consisting of COX15, ferredoxin and ferredoxin reductase
- Gene Name:
- COX15
- Uniprot ID:
- P40086
- Molecular weight:
- 54657.89844
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- PUT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07275
- Molecular weight:
- 64434.60156
Reactions
| (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O → L-glutamate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is suggested to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway
- Gene Name:
- ERG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32476
- Molecular weight:
- 55125.39844
Reactions
| Squalene + AH(2) + O(2) → (S)-squalene-2,3-epoxide + A + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in ubiquinone biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Component of the coenzyme Q biosynthetic pathway. May play a role in organizing a multi-subunit COQ enzyme complex required for coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Required for steady-state levels of COQ3, COQ4, COQ6, COQ7 and COQ9 polypeptides
- Gene Name:
- COQ4
- Uniprot ID:
- O13525
- Molecular weight:
- 38626.80078
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the dehydration of cis-homoaconitate to homoisocitric acid
- Gene Name:
- LYS4
- Uniprot ID:
- P49367
- Molecular weight:
- 75150.10156
Reactions
| (1R,2S)-1-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate → (Z)-but-1-ene-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in uroporphyrinogen-III synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes cyclization of the linear tetrapyrrole, hydroxymethylbilane, to the macrocyclic uroporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- HEM4
- Uniprot ID:
- P06174
- Molecular weight:
- 30911.30078
Reactions
| Hydroxymethylbilane → uroporphyrinogen III + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTP cyclohydrolase II activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of GTP to 2,5-diamino-6- ribosylamino-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate (DARP), formate and pyrophosphate
- Gene Name:
- RIB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38066
- Molecular weight:
- 38331.60156
Reactions
| GTP + 3 H(2)O → formate + 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidine + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in gamma-glutamyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in the turnover of the vacuolar glutathione and in the supply of growth requirements during nitrogen starvation
- Gene Name:
- ECM38
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05902
- Molecular weight:
- 73179.79688
Reactions
| (5-L-glutamyl)-peptide + an amino acid → peptide + 5-L-glutamyl amino acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Thiolesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of S-D- lactoyl-glutathione to form glutathione and D-lactic acid
- Gene Name:
- GLO2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05584
- Molecular weight:
- 31326.30078
Reactions
| S-(2-hydroxyacyl)glutathione + H(2)O → glutathione + a 2-hydroxy carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Monothiol glutaredoxin involved in iron-sulfur biogenesis. Required for normal iron homeostasis. Protects cells against oxidative damage due to reactive oxygen species
- Gene Name:
- GRX5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02784
- Molecular weight:
- 16931.30078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in glutathione peroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in oxidative stress response and redox homeostasis. Functions as a sensor and transducer of hydroperoxide stress. In response to hydroperoxide stress it oxidizes (activates) the transcription activator YAP1, which is involved in transcription activation of genes of the oxidative stress response pathway. May also play a direct role in hydroperoxide scavenging, being the most active of three closely related S.cerevisiae peroxiredoxins (GPX1, GPX2, and HYP1/GPX3) with respect to peroxide and lipid hydroperoxide reduction. The three enzymes are not required for the glutaredoxin-mediated antioxidant function. In the presence of peroxides, HYP1 is directly oxidized at Cys-36 to form a cysteine sulfenic acid (-SOH). Cys-36-SOH then forms either an intramolecular disulfide bond (Cys-36 with Cys-82) or a transient, intermolecular disulfide bond with 'Cys-598' of YAP1, which is further resolved into a YAP1 intramolecular disulfide bond ('Cys-303' with 'Cys-598') and a reduced Cys-36 in HYP1/GPX3
- Gene Name:
- HYR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40581
- Molecular weight:
- 18641.40039
Reactions
| 2 R'-SH + ROOH → R'-S-S-R' + H(2)O + ROH. |
| 2 glutathione + a lipid hydroperoxide → glutathione disulfide + lipid + H2O |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme with glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S- transferase (GST) activity. The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing cytosolic protein- and non-protein-disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Required for resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by directly reducing hydroperoxides and for the detoxification of ROS-mediated damage
- Gene Name:
- GRX2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17695
- Molecular weight:
- 15861.2998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in carboxylesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Serine hydrolase involved in the detoxification of formaldehyde
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P40363
- Molecular weight:
- 33934.0
Reactions
| S-formylglutathione + H(2)O → glutathione + formate. |
| 4-methylumbelliferyl acetate + H2O → 4-methylumbelliferone + acetate |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Thiolesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of S-D- lactoyl-glutathione to form glutathione and D-lactic acid
- Gene Name:
- GLO4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12320
- Molecular weight:
- 32338.59961
Reactions
| S-(2-hydroxyacyl)glutathione + H(2)O → glutathione + a 2-hydroxy carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme with glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S- transferase (GST) activity. The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing cytosolic protein- and non-protein-disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Required for resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by directly reducing hydroperoxides and for the detoxification of ROS-mediated damage
- Gene Name:
- GRX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25373
- Molecular weight:
- 12380.09961
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in riboflavin biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Condensation of 5-amino-6-(1'-D)-ribityl-amino- 2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione with L-3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4- phosphate to produce 6,7-dimethyl-8-(1-D-ribityl)lumazine
- Gene Name:
- RIB4
- Uniprot ID:
- P50861
- Molecular weight:
- 18555.40039
Reactions
| 2 6,7-dimethyl-8-(1-D-ribityl)lumazine → riboflavin + 4-(1-D-ribitylamino)-5-amino-2,6-dihydroxypyrimidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the provision of inositol required for synthesis of phosphatidylinositol and polyphosphoinositides and involved in the inositol cycle of calcium signaling
- Gene Name:
- INM2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05533
- Molecular weight:
- 32092.40039
Reactions
| Myo-inositol phosphate + H(2)O → myo-inositol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, disulfide as acceptor
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PDA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16387
- Molecular weight:
- 46342.69922
Reactions
| Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine → [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first step in the removal of the two C-4 methyl groups of 4,4-dimethylzymosterol
- Gene Name:
- ERG25
- Uniprot ID:
- P53045
- Molecular weight:
- 36478.89844
Reactions
| 4,4-dimethyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
| 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O. |
| 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for growth under anaerobic conditions
- Gene Name:
- NPT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39683
- Molecular weight:
- 49018.19922
Reactions
| Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate → nicotinate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ferroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Promotes the biosynthesis of heme as well as the assembly and repair of iron-sulfur clusters by delivering Fe(2+) to proteins involved in these pathways. Plays a role in the protection against iron-catalyzed oxidative stress through its ability to catalyze the oxidation of Fe(2+) to Fe(3+). Can store large amounts of the metal in the form of a ferrihydrite mineral by oligomerization. May be involved in regulation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain
- Gene Name:
- YFH1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07540
- Molecular weight:
- 19490.0
Reactions
| 4 Fe(2+) + 4 H(+) + O(2) → 4 Fe(3+) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in allantoinase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32375
- Molecular weight:
- 50125.89844
Reactions
| (S)-allantoin + H(2)O → allantoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism:it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA
- Gene Name:
- DUT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P33317
- Molecular weight:
- 15307.2002
Reactions
| dUTP + H(2)O → dUMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates as a hydrogen donor in redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. It is involved in many cellular processes, including deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, repair of oxidatively damaged proteins, protein folding, sulfur metabolism, and redox homeostasis. Thioredoxin-dependent enzymes include phosphoadenosine-phosphosulfate reductase MET16, alkyl- hydroperoxide reductase DOT5, thioredoxin peroxidases TSA1 and TSA2, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase AHP1, and peroxiredoxin HYR1. Thioredoxin is also involved in protection against reducing stress. As part of the LMA1 complex, it is involved in the facilitation of vesicle fusion such as homotypic vacuole and ER- derived COPII vesicle fusion with the Golgi. This activity does not require the redox mechanism. Through its capacity to inactivate the stress response transcription factor YAP1 and its regulator the hydroperoxide stress sensor HYR1, it is involved in feedback regulation of stress response gene expression upon oxidative stress
- Gene Name:
- TRX2
- Uniprot ID:
- P22803
- Molecular weight:
- 11203.7998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates as a hydrogen donor in redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. It is involved in many cellular processes, including deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, repair of oxidatively damaged proteins, protein folding, sulfur metabolism, and redox homeostasis. Thioredoxin-dependent enzymes include phosphoadenosine-phosphosulfate reductase MET16, alkyl- hydroperoxide reductase DOT5, thioredoxin peroxidases TSA1 and TSA2, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase AHP1, and peroxiredoxin HYR1. Thioredoxin is also involved in protection against reducing stress. As part of the LMA1 complex, it is involved in the facilitation of vesicle fusion such as homotypic vacuole and ER- derived COPII vesicle fusion with the Golgi. This activity does not require the redox mechanism
- Gene Name:
- TRX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22217
- Molecular weight:
- 11234.90039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Synthase catalytic subunit of the trehalose synthase complex that catalyzes the production of trehalose from glucose-6- phosphate and UDP-glucose in a two step process. Can function independently of the complex
- Gene Name:
- TPS1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q00764
- Molecular weight:
- 56147.5
Reactions
| UDP-glucose + D-glucose 6-phosphate → UDP + alpha,alpha-trehalose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the gamma-elimination of phosphate from L- phosphohomoserine and the beta-addition of water to produce L- threonine
- Gene Name:
- THR4
- Uniprot ID:
- P16120
- Molecular weight:
- 57473.69922
Reactions
| O-phospho-L-homoserine + H(2)O → L-threonine + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in energy production. Its activity is stimulated by uncouplers of ATP synthesis
- Gene Name:
- PPA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P28239
- Molecular weight:
- 35572.39844
Reactions
| Diphosphate + H(2)O → 2 phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in DNA binding
- Specific function:
- Integrase (IN) targets the VLP to the nucleus, where a subparticle preintegration complex (PIC) containing at least integrase and the newly synthesized dsDNA copy of the retrotransposon must transit the nuclear membrane. Once in the nucleus, integrase performs the integration of the dsDNA into the host genome
- Gene Name:
- TY2B-OR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12113
- Molecular weight:
- 201982.0
Reactions
| Deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) → diphosphate + DNA(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Diphosphate + H(2)O = 2 phosphate
- Gene Name:
- IPP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00817
- Molecular weight:
- 32299.30078
Reactions
| Diphosphate + H(2)O → 2 phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in protoheme IX farnesyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts protoheme IX and farnesyl diphosphate to heme O
- Gene Name:
- COX10
- Uniprot ID:
- P21592
- Molecular weight:
- 52147.19922
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- PHO3
- Uniprot ID:
- P24031
- Molecular weight:
- 52776.10156
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Required for meiosis and spore formation. Seems to be involved in the coordinate induction of late meiotic events. PLD activity is induced under sporulation conditions and seems to be necessary to complete the meiotic cycle, but not for vegetative cell growth
- Gene Name:
- SPO14
- Uniprot ID:
- P36126
- Molecular weight:
- 195202.0
Reactions
| A phosphatidylcholine + H(2)O → choline + a phosphatidate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-formyl-L-kynurenine to L- kynurenine, the second step in the conversion of tryptophan to nicotinic acid, NAD(H) and NADP(H)
- Gene Name:
- BNA7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04066
- Molecular weight:
- 29991.0
Reactions
| N-formyl-L-kynurenine + H(2)O → formate + L-kynurenine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- UGA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38067
- Molecular weight:
- 54188.80078
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → succinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate = 3-methyl-2- oxobutanoate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ILV3
- Uniprot ID:
- P39522
- Molecular weight:
- 62860.60156
Reactions
| 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate → 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. RNR4 is required for proper folding of RNR2 and assembly with the large subunits
- Gene Name:
- RNR4
- Uniprot ID:
- P49723
- Molecular weight:
- 40054.19922
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- After transfer of sugars to endogenous macromolecular acceptors, the enzyme converts nucleoside diphosphates to nucleoside monophosphates which in turn exit the Golgi lumen in a coupled antiporter reaction, allowing entry of additional nucleotide sugar from the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- GDA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32621
- Molecular weight:
- 56821.0
Reactions
| GDP + H(2)O → GMP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes an epoxide moiety of LTA(4) to form LTB(4). The enzyme also has aminopeptidase activity
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q10740
- Molecular weight:
- 77352.10156
Reactions
| (7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-(5S,6S)-5,6-epoxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoate + H(2)O → (6Z,8E,10E,14Z)-(5S,12R)-5,12-dihydroxyicosa-6,8,10,14-tetraenoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1->4)- linked alpha-D-glucose residues with release of alpha-D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- MAL32
- Uniprot ID:
- P38158
- Molecular weight:
- 68141.79688
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Successive hydrolysis of beta-D-glucose units from the non-reducing ends of (1->3)-beta-D-glucans, releasing alpha-glucose
- Gene Name:
- EXG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P52911
- Molecular weight:
- 63507.60156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Probably involved in the processes of spore formation and contributes to ascospore thermoresistance by participating in the morphogenesis of ascospore walls. The enzyme may do this by modifying glucan linkages in the developing ascospore wall, thus strengthening it or lending it plasticity
- Gene Name:
- SPR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32603
- Molecular weight:
- 51809.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalytic subunit of glucosidase 2, which cleaves sequentially the 2 innermost alpha-1,3-linked glucose residues from the Glc(2)Man(9)GlcNAc(2) oligosaccharide precursor of immature glycoproteins
- Gene Name:
- ROT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38138
- Molecular weight:
- 110265.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1->4)- linked alpha-D-glucose residues with release of alpha-D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- MAL12
- Uniprot ID:
- P53341
- Molecular weight:
- 68093.70313
Reactions
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Probable alpha-glucosidase involved in maltose metabolism
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P40439
- Molecular weight:
- 68698.10156
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Glucanases possibly play a role in cell expansion during growth, in cell-cell fusion during mating, and in spore release during sporulation. This enzyme hydrolyzes both 1,3-beta- and 1,6- beta-linkages and even has beta-glucosidase activity. It could also function biosynthetically as a transglycosylase
- Gene Name:
- EXG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23776
- Molecular weight:
- 51310.5
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1->4)- linked alpha-D-glucose residues with release of alpha-D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- MAL62
- Uniprot ID:
- P07265
- Molecular weight:
- 68182.79688
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Glucanases possibly play a role in cell expansion during growth, in cell-cell fusion during mating, and in spore release during sporulation. This enzyme may be involved in beta-glucan degradation and also function biosynthetically as a transglycosylase
- Gene Name:
- BGL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P15703
- Molecular weight:
- 34118.30078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ERR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12007
- Molecular weight:
- 47327.10156
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ERR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P42222
- Molecular weight:
- 47312.10156
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ENO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00924
- Molecular weight:
- 46815.69922
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- ENO2
- Uniprot ID:
- P00925
- Molecular weight:
- 46913.69922
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate phosphatase required for efficient ceramide synthesis from exogenous sphingoid bases. Involved in endocytosis and calcium-mediated signaling
- Gene Name:
- LCB3
- Uniprot ID:
- P47013
- Molecular weight:
- 47371.30078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate phosphatase required for efficient ceramide synthesis from exogenous sphingoid bases. Involved in endocytosis and calcium-mediated signaling
- Gene Name:
- YSR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P23501
- Molecular weight:
- 46487.69922
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Required for hydroxylation of C-4 in the sphingoid moiety of ceramide. Involved in the response to syringomycin
- Gene Name:
- SUR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38992
- Molecular weight:
- 40734.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P10594
- Molecular weight:
- 60569.89844
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC3
- Uniprot ID:
- P10595
- Molecular weight:
- 8649.90039
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme acting as 1,4-alpha-D-glucan:1,4- alpha-D-glucan 4-alpha-D-glycosyltransferase and amylo-1,6- glucosidase in glycogen degradation
- Gene Name:
- GDB1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06625
- Molecular weight:
- 174970.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal (1->4)-linked alpha-D- glucose residues successively from non-reducing ends of the chains with release of beta-D-glucose
- Gene Name:
- SGA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08019
- Molecular weight:
- 61462.39844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC4
- Uniprot ID:
- P10596
- Molecular weight:
- 60574.80078
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC5
- Uniprot ID:
- P10597
- Molecular weight:
- 8649.90039
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC2
- Uniprot ID:
- P00724
- Molecular weight:
- 60638.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the dissoultion of the mother-daughter septum during cell separation
- Gene Name:
- DSE4
- Uniprot ID:
- P53753
- Molecular weight:
- 121063.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Preferentially hydrolyzes isomaltose, with little activity towards isomaltotriose or longer oligosaccharides. Does not hydrolyze maltose
- Gene Name:
- FSP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P53051
- Molecular weight:
- 68591.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- The production of the second messenger molecules diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) is mediated by activated phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzymes. Required for cell growth, osmoresistance and expression of GPD1
- Gene Name:
- PLC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32383
- Molecular weight:
- 100547.0
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + diacylglycerol. |
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls the cellular levels and subcellular distribution of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Plays an essential role in a TGN (trans Golgi network)-to-early endosome pathway. Involved in clathrin-mediated protein sorting at the TGN
- Gene Name:
- INP53
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12271
- Molecular weight:
- 124576.0
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + phosphate. |
| D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + H2O → D-myo-inositol 1,4-bisphosphate + phosphate |
| D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate + H2O → D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls the cellular levels and subcellular distribution of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Specifically functions within the early endocytic pathway and actin organization
- Gene Name:
- INP52
- Uniprot ID:
- P50942
- Molecular weight:
- 133330.0
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + phosphate. |
| D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + H2O → D-myo-inositol 1,4-bisphosphate + phosphate |
| D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate + H2O → D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Active on 2-DOG-6P, also very active on fructose-1P
- Gene Name:
- DOG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38774
- Molecular weight:
- 27099.59961
Reactions
| 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate + H(2)O → 2-deoxy-D-glucose + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Active on 2-DOG-6P, not very active on fructose-1p
- Gene Name:
- DOG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38773
- Molecular weight:
- 27164.80078
Reactions
| 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate + H(2)O → 2-deoxy-D-glucose + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Regulatory subunit of the trehalose synthase complex that catalyzes the production of trehalose from glucose-6- phosphate and UDP-glucose in a two step process. May stabilize the trehalose synthase complex
- Gene Name:
- TPS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38426
- Molecular weight:
- 118834.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in glycogen (starch) synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Transfers the glycosyl residue from UDP-Glc to the non- reducing end of alpha-1,4-glucan. Is believed to regulate the synthesis of glycogen
- Gene Name:
- GSY2
- Uniprot ID:
- P27472
- Molecular weight:
- 80078.20313
Reactions
| UDP-glucose ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n) → UDP + ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in glycogen (starch) synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Transfers the glycosyl residue from UDP-Glc to the non- reducing end of alpha-1,4-glucan. Is believed to regulate the synthesis of glycogen
- Gene Name:
- GSY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23337
- Molecular weight:
- 80509.60156
Reactions
| UDP-glucose ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n) → UDP + ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Sequentially removes both fatty acyl groups from diacylglycerophospholipids and therefore has both phospholipase A and lysophospholipase activities. Substrate preference is phosphatidylserine > phosphatidylinositol. Does not cleave phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylinositol-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- PLB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08108
- Molecular weight:
- 75076.20313
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O → glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Sequentially removes both fatty acyl groups from diacylglycerophospholipids and therefore has both phospholipase A and lysophospholipase activities. Substrate preference is phosphatidylserine > phosphatidylinositol >> phosphatidylcholine > phosphatidylethanolamine
- Gene Name:
- PLB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39105
- Molecular weight:
- 71666.60156
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O → glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Intracellular phospholipase B that catalyzes the double deacylation of phosphatidylcholine (PC) to glycerophosphocholine (GroPCho). Plays an important role in membrane lipid homeostasis. Responsible for the rapid PC turnover in response to inositol, elevated temperatures, or when choline is present in the growth medium
- Gene Name:
- NTE1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04958
- Molecular weight:
- 187131.0
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O → glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Sequentially removes both fatty acyl groups from diacylglycerophospholipids and therefore has both phospholipase A and lysophospholipase activities. Substrate preference is phosphatidylserine > phosphatidylinositol > phosphatidylcholine > phosphatidylethanolamine
- Gene Name:
- PLB2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03674
- Molecular weight:
- 75454.60156
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O → glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on a sulfur group of donors, disulfide as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Has an important function as a repair enzyme for proteins that have been inactivated by oxidation. Catalyzes the reversible oxidation-reduction of methionine sulfoxide in proteins to methionine. Also able to reduce dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as well, with DMS as the product
- Gene Name:
- MXR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40029
- Molecular weight:
- 21140.69922
Reactions
| Peptide-L-methionine + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → peptide-L-methionine (S)-S-oxide + thioredoxin. |
| L-methionine + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → L-methionine (S)-S-oxide + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminopeptidase activity
- Specific function:
- Removes the amino-terminal methionine from nascent proteins
- Gene Name:
- MAP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01662
- Molecular weight:
- 43373.0
- General function:
- Involved in aminopeptidase activity
- Specific function:
- Removes the amino-terminal methionine from nascent proteins
- Gene Name:
- MAP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38174
- Molecular weight:
- 47502.19922
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the interconversion of 2-phosphoglycerate and 3-phosphoglycerate
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12040
- Molecular weight:
- 26176.5
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → 3-phospho-D-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Could be non-functional
- Gene Name:
- GPM2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12008
- Molecular weight:
- 36072.80078
Reactions
| 2-phospho-D-glycerate → 3-phospho-D-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- IMP-specific 5'-nucleotidase involved in IMP (inositol monophosphate) degradation
- Gene Name:
- ISN1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99312
- Molecular weight:
- 51329.5
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in GTP cyclohydrolase I activity
- Specific function:
- GTP + H(2)O = formate + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6- (erythro-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-dihydropteridine triphosphate
- Gene Name:
- FOL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P51601
- Molecular weight:
- 27768.80078
Reactions
| GTP + H(2)O → formate + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-(erythro-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-dihydropteridine triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme is required for electron transfer from NADP to cytochrome P450 in microsomes. It can also provide electron transfer to heme oxygenase and cytochrome B5
- Gene Name:
- NCP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16603
- Molecular weight:
- 76771.10156
Reactions
| NADPH + n oxidized hemoprotein → NADP(+) + n reduced hemoprotein. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on thioredoxins 1 and 2
- Gene Name:
- TRR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P29509
- Molecular weight:
- 34237.80078
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) → thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on mitochondrial thioredoxin 3. Implicated in the defense against oxidative stress
- Gene Name:
- TRR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38816
- Molecular weight:
- 37087.0
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) → thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain
- Gene Name:
- CYC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00044
- Molecular weight:
- 12181.90039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain
- Gene Name:
- CYC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P00045
- Molecular weight:
- 12532.2998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Regulates the phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-diphosphate levels on the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum and thereby regulates secretion
- Gene Name:
- INP54
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08227
- Molecular weight:
- 43798.69922
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoric ester hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- The PI(3,5)P2 regulatory complex regulates both the synthesis and turnover of phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,5)P2). Major enzyme required for hyperosmotic shock- induced turnover of PtdIns(3,5)P2 and requires VAC14 for this function. In vivo, mediates turnover of PtdIns(3,5)P2 at the vacuole membrane necessary for vacuolar size control. In vitro, catalyzes the removal of phosphate from the fifth hydroxyl of the myo-inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- FIG4
- Uniprot ID:
- P42837
- Molecular weight:
- 101745.0
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the metabolism of ADP-ribose 1',2'-cyclic phosphate which is produced as a consequence of tRNA splicing
- Gene Name:
- CPD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53314
- Molecular weight:
- 26731.40039
Reactions
| Nucleoside 2',3'-cyclic phosphate + H(2)O → nucleoside 2'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoric ester hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphoinositide phosphatase that hydrolyzes PtdIns(3)P and PtdIns(4)P. Has low activity towards PtdIns(3,5)P2. May be involved in the coordination of the activities of the secretory pathway and the actin cytoskeleton
- Gene Name:
- SAC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32368
- Molecular weight:
- 71124.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the control of phosphotidylinositol 3- phosphate (PI(3)P)-dependent signaling and in the maintenance of endosomal system integrity
- Gene Name:
- YMR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P47147
- Molecular weight:
- 80151.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilizes O(2) and electrons from the reduced cytochrome b(5) domain to catalyze the insertion of a double bond into a spectrum of fatty acyl-CoA substrates (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- OLE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21147
- Molecular weight:
- 58402.60156
Reactions
| Stearoyl-CoA + 2 ferrocytochrome b5 + O(2) + 2 H(+) → oleoyl-CoA + 2 ferricytochrome b5 + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Ceramide hydroxylase involved in the alpha-hydroxylation of sphingolipid-associated very long chain fatty acids. Hydroxylates the very long chain fatty acid of ceramides at C2 and C3
- Gene Name:
- SCS7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03529
- Molecular weight:
- 44881.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls the cellular levels and subcellular distribution of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Plays an essential role in a TGN (trans Golgi network)-to-early endosome pathway. Involved in endocytosis and acts as a negative regulator of the Slm pathway which modulates polarized actin assembly and growth
- Gene Name:
- INP51
- Uniprot ID:
- P40559
- Molecular weight:
- 108429.0
Reactions
| 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H(2)O → 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dephosphorylation of diacylglycerol phosphate (DGPP) to phosphatidate (PA) and the subsequent dephosphorylation of PA to diacylglycerol (DAG). Together with DPP1, regulates intracellular DGPP and PA levels which are phospholipid molecules believed to play a signaling role in stress response. Can also use lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) as a substrate. Substrate preference is PA > DGPP > LPA
- Gene Name:
- LPP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04396
- Molecular weight:
- 31585.90039
Reactions
| A 1,2-diacylglycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O → a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + phosphate. |
| Diacylglycerol pyrophosphate + H(2)O → phosphatidate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a crucial role in the hydrolysis of isoamyl acetate in sake mash
- Gene Name:
- IAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P41734
- Molecular weight:
- 27346.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the introduction of a C-5 double bond in the B ring of ergosterol. May contribute to the regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- ERG3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32353
- Molecular weight:
- 42729.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dephosphorylation of diacylglycerol phosphate (DGPP) to phosphatidate (PA) and the subsequent dephosphorylation of PA to diacylglycerol (DAG). Together with LPP1, regulates intracellular DGPP and PA levels which are phospholipid molecules believed to play a signaling role in stress response. Can also use lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) as a substrate. Substrate preference is DGPP > LPA > PA
- Gene Name:
- DPP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05521
- Molecular weight:
- 33513.60156
Reactions
| A 1,2-diacylglycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O → a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + phosphate. |
| Diacylglycerol pyrophosphate + H(2)O → phosphatidate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TRX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P25372
- Molecular weight:
- 14432.0
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide
- Gene Name:
- CTT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06115
- Molecular weight:
- 64583.0
Reactions
| 2 H(2)O(2) → O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide
- Gene Name:
- CTA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15202
- Molecular weight:
- 58555.19922
Reactions
| 2 H(2)O(2) → O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipid metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Mediates the hydrolysis of steryl esters. Required for mobilization of steryl ester, thereby playing a central role in lipid metabolism. May have weak lipase activity toward triglycerides upon some conditions, however, the relevance of such activity is unclear in vivo
- Gene Name:
- TGL1
- Uniprot ID:
- P34163
- Molecular weight:
- 62978.39844
Reactions
| A steryl ester + H(2)O → a sterol + a fatty acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipid metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Mediates the hydrolysis of steryl esters, thereby playing a central role in lipid metabolism. Under heme-deficient conditions, it constitutes the major steryl ester hydrolase, suggesting that it plays a central role in mobilization of steryl esters under anaerobic conditions
- Gene Name:
- YEH1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07804
- Molecular weight:
- 66507.39844
Reactions
| A steryl ester + H(2)O → a sterol + a fatty acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipid metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Mediates the hydrolysis of steryl esters. Required for mobilization of steryl ester, thereby playing a central role in lipid metabolism
- Gene Name:
- YEH2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07950
- Molecular weight:
- 62446.0
Reactions
| A steryl ester + H(2)O → a sterol + a fatty acid. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- ATPase required for the post-translational delivery of tail-anchored (TA) proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. Recognizes and selectively binds the transmembrane domain of TA proteins in the cytosol. This complex then targets to the endoplasmic reticulum by membrane-bound receptors GET1 and GET2, where the tail-anchored protein is released for insertion. This process is regulated by ATP binding and hydrolysis. ATP binding drives the homodimer towards the closed dimer state, facilitating recognition of newly synthesized TA membrane proteins. ATP hydolysis is required for insertion. Subsequently, the homodimer reverts towards the open dimer state, lowering its affinity for the GET1-GET2 receptor, and returning it to the cytosol to initiate a new round of targeting. Cooperates with the HDEL receptor ERD2 to mediate the ATP-dependent retrieval of resident ER proteins that contain a C-terminal H-D-E-L retention signal from the Golgi to the ER. Involved in low-level resistance to the oxyanions arsenite and arsenate, and in heat tolerance
- Gene Name:
- GET3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12154
- Molecular weight:
- 39353.39844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in polygalacturonase activity
- Specific function:
- Random hydrolysis of (1->4)-alpha-D- galactosiduronic linkages in pectate and other galacturonans
- Gene Name:
- PGU1
- Uniprot ID:
- P47180
- Molecular weight:
- 37286.60156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds
- Specific function:
- Lipolytic activity towards triacylglycerols and diacylglycerols with short-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- TGL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54857
- Molecular weight:
- 37499.89844
Reactions
| Triacylglycerol + H(2)O → diacylglycerol + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in triglyceride lipase activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for lysis of subvacuolar cytoplasm to vacuole targeted bodies and intravacuolar autophagic bodies. Involved in the lysis of intravacuolar multivesicular body (MVB) vesicles
- Gene Name:
- ATG15
- Uniprot ID:
- P25641
- Molecular weight:
- 58434.5
Reactions
| Triacylglycerol + H(2)O → diacylglycerol + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Releases specific fatty acids from neutral lipid triacylglycerols (TAG) thereby supplying fatty acids to a general acylation process
- Gene Name:
- TGL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P40308
- Molecular weight:
- 73611.79688
Reactions
| Triacylglycerol + H(2)O → diacylglycerol + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Releases specific fatty acids from neutral lipid triacylglycerols (TAG) thereby supplying fatty acids to a general acylation process. May have a specific role in sporulation
- Gene Name:
- TGL5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12043
- Molecular weight:
- 84715.10156
Reactions
| Triacylglycerol + H(2)O → diacylglycerol + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Releases specific fatty acids from neutral lipid triacylglycerols (TAG) thereby supplying fatty acids to a general acylation process. May have a specific role in sporulation
- Gene Name:
- TGL4
- Uniprot ID:
- P36165
- Molecular weight:
- 102716.0
Reactions
| Triacylglycerol + H(2)O → diacylglycerol + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the hydrolysis of the phosphosphingolipids (IPS), inositol phosphorylceramide (IPC), mannosylinositol phosphorylceramide (MIPC), and mannosyldiinositol phosphorylceramide (M(IP)2C). Also active on sphingomyelin, but this activity is probably not physiologically relevant
- Gene Name:
- ISC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40015
- Molecular weight:
- 53939.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Degrades free oligosaccharides in the vacuole
- Gene Name:
- AMS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22855
- Molecular weight:
- 124498.0
- General function:
- Involved in nucleic acid binding
- Specific function:
- Constitutes one of the two catalytic subunit of the tRNA-splicing endonuclease complex, a complex responsible for identification and cleavage of the splice sites in pre-tRNA. It cleaves pre-tRNA at the 5'- and 3'-splice sites to release the intron. The products are an intron and two tRNA half-molecules bearing 2',3' cyclic phosphate and 5'-OH termini. There are no conserved sequences at the splice sites, but the intron is invariably located at the same site in the gene, placing the splice sites an invariant distance from the constant structural features of the tRNA body. It probably carries the active site for 3'-splice site cleavage
- Gene Name:
- SEN34
- Uniprot ID:
- P39707
- Molecular weight:
- 31312.69922
- General function:
- Involved in nucleic acid binding
- Specific function:
- Constitutes one of the two catalytic subunit of the tRNA-splicing endonuclease complex, a complex responsible for identification and cleavage of the splice sites in pre-tRNA. It cleaves pre-tRNA at the 5'- and 3'-splice sites to release the intron. The products are an intron and two tRNA half-molecules bearing 2',3' cyclic phosphate and 5'-OH termini. There are no conserved sequences at the splice sites, but the intron is invariably located at the same site in the gene, placing the splice sites an invariant distance from the constant structural features of the tRNA body. This subunit may anchor the endonuclease complex to the nuclear membrane. Probably carries the active site for 5'-splice site cleavage
- Gene Name:
- SEN2
- Uniprot ID:
- P16658
- Molecular weight:
- 44109.0
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Transfers a segment of a (1->4)-alpha-D-glucan chain to a primary hydroxy group in a similar glucan chain
- Gene Name:
- GLC3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32775
- Molecular weight:
- 81114.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in peroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- CCP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00431
- Molecular weight:
- 40352.69922
Reactions
| 2 ferrocytochrome c + H(2)O(2) → 2 ferricytochrome c + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in enoyl-CoA hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the dehydration step in very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) synthesis
- Gene Name:
- PHS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40857
- Molecular weight:
- 24510.40039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylglycerophosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase involved in the biosynthesis of cardiolipin (CL), a unique dimeric phosphoglycerolipid predominantly present in mitochondrial membranes and which has important functions for cellular energy metabolism, mitochondrial dynamics and the initiation of apoptotic pathways. Required for the stability of respiratory chain supercomplexes and for growth at elevated temperature, in presence of ethidium bromide or in absence of prohibitins
- Gene Name:
- GEP4
- Uniprot ID:
- P38812
- Molecular weight:
- 20944.90039
Reactions
| Phosphatidylglycerophosphate + H(2)O → phosphatidylglycerol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminoacyl-tRNA hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA + H(2)O = N- substituted amino acid + tRNA
- Gene Name:
- PTH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38876
- Molecular weight:
- 21036.0
Reactions
| N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA + H(2)O → N-substituted amino acid + tRNA. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on tyrosine phosphorylated proteins, low-MW aryl phosphates and natural and synthetic acyl phosphates
- Gene Name:
- LTP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40347
- Molecular weight:
- 18675.09961
Reactions
| Protein tyrosine phosphate + H(2)O → protein tyrosine + phosphate. |
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminoacyl-tRNA hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- The natural substrate for this enzyme may be peptidyl- tRNAs which drop off the ribosome during protein synthesis
- Gene Name:
- PTH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P34222
- Molecular weight:
- 23128.0
Reactions
| N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA + H(2)O → N-substituted amino acid + tRNA. |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- PHO12
- Uniprot ID:
- P38693
- Molecular weight:
- 52699.30078
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O → an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing N-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Also acts on cytidine
- Gene Name:
- URH1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04179
- Molecular weight:
- 37960.0
Reactions
| Uridine + H(2)O → D-ribose + uracil. |
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of S-adenosylmethionine from methionine and ATP
- Gene Name:
- SAM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P19358
- Molecular weight:
- 42255.5
Reactions
| ATP + L-methionine + H(2)O → phosphate + diphosphate + S-adenosyl-L-methionine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12486
- Molecular weight:
- 24839.80078
Reactions
| 2-Phosphoglycolate + H2O → glycolate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04223
- Molecular weight:
- 35278.10156
Reactions
| 2-Phosphoglycolate + H2O → glycolate + phosphate |
- General function:
- Involved in endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase activity
- Specific function:
- Endohydrolysis of (1->3)- or (1->4)-linkages in beta-D-glucans when the glucose residue whose reducing group is involved in the linkage to be hydrolyzed is itself substituted at C-3
- Gene Name:
- ACF2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12168
- Molecular weight:
- 88402.5
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Involved in cell separation
- Gene Name:
- SCW11
- Uniprot ID:
- P53189
- Molecular weight:
- 56446.0
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides
- Gene Name:
- RNR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P21672
- Molecular weight:
- 97513.79688
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O → ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the provision of inositol required for synthesis of phosphatidylinositol and polyphosphoinositides
- Gene Name:
- INM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38710
- Molecular weight:
- 32823.0
Reactions
| Myo-inositol phosphate + H(2)O → myo-inositol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in prephenate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Prephenate = phenylpyruvate + H(2)O + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PHA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P32452
- Molecular weight:
- 38224.80078
Reactions
| Prephenate → phenylpyruvate + H(2)O + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydropteroate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes three sequential steps of tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- FOL1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53848
- Molecular weight:
- 93119.10156
Reactions
| 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-(D-erythro-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-7,8-dihydropteridine → 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropteridine + glycolaldehyde. |
| ATP + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropteridine → AMP + (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate. |
| (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate + 4-aminobenzoate → diphosphate + dihydropteroate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Electron donor reductase for cytochrome b5. The cytochrome b5/NADH cytochrome b5 reductase electron transfer system supports the catalytic activity of several sterol biosynthetic enzymes. Plays a role in bud morphology
- Gene Name:
- CBR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38626
- Molecular weight:
- 31493.59961
Reactions
| NADH + 2 ferricytochrome b5 → NAD(+) + H(+) + 2 ferrocytochrome b5. |
- General function:
- Involved in 6-phosphogluconolactonase activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6- phosphogluconate
- Gene Name:
- SOL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38858
- Molecular weight:
- 27784.19922
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + H(2)O → 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D- fructofuranoside residues in beta-D-fructofuranosides
- Gene Name:
- SUC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P07635
- Molecular weight:
- 11248.90039
- General function:
- triglyceride metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Converts monoacylglycerides (MAG) to free fatty acids and glycerol. Required for efficient degradation of MAG, short-lived intermediates of glycerolipid metabolism which may also function as lipid signaling molecules. Controls inactivation of the signaling lipid N-palmitoylethanolamine (PEA).
- Gene Name:
- YJU3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28321
- Molecular weight:
- 35562.4
Reactions
- General function:
- vacuole fusion, non-autophagic
- Specific function:
- Mg(2+)-dependent phosphatidate (PA) phosphatase which catalyzes the dephosphorylation of PA to yield diacylglycerol. Required for de novo lipid synthesis and formation of lipid droplets. Controles transcription of phospholipid biosynthetic genes and nuclear structure by regulating the amount of membrane present at the nuclear envelope. Involved in plasmid maintenance, in respiration and in cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- PAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32567
- Molecular weight:
- 95029.985
Reactions
- General function:
- ribosome biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase involved in riboneogenesis. Dephosphorylates sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (SBP), which is converted via the non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway to ribose-5-phosphate. Has a fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase activity in vitro, but this is probably not biologically relevant, since deletion does not affect fructose 1,6-biphosphate (FBP) levels.
- Gene Name:
- SHB17
- Uniprot ID:
- P36136
- Molecular weight:
- 31021.71
Reactions
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of the sodium or lithium ions to allow salt tolerance. Is negatively modulated by SIS2/HAL3
- Gene Name:
- ENA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13587
- Molecular weight:
- 120356.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Na(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + Na(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of sodium or lithium ions to allow salt tolerance
- Gene Name:
- ENA5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12691
- Molecular weight:
- 120295.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Na(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + Na(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of sodium or lithiums ions to allow salt tolerance
- Gene Name:
- ENA2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01896
- Molecular weight:
- 120316.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Na(+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + Na(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium. Has a role in the secretory pathway
- Gene Name:
- PMR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13586
- Molecular weight:
- 104570.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ca(2+)(Cis) → ADP + phosphate + Ca(2+)(Trans). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium. Transports the calcium to the vacuole and participates in the control of the cytosolic free calcium
- Gene Name:
- PMC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38929
- Molecular weight:
- 130860.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ca(2+)(Cis) → ADP + phosphate + Ca(2+)(Trans). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of phospholipids (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- DNF3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12674
- Molecular weight:
- 188318.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phospholipid(In) → ADP + phosphate + phospholipid(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of phospholipids. Required for protein transport from Golgi to vacuoles
- Gene Name:
- DNF2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12675
- Molecular weight:
- 182617.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phospholipid(In) → ADP + phosphate + phospholipid(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of phospholipids (Potential). Seems to be involved in ribosome assembly
- Gene Name:
- DRS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P39524
- Molecular weight:
- 153843.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phospholipid(In) → ADP + phosphate + phospholipid(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of phospholipids (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- DNF1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32660
- Molecular weight:
- 177796.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phospholipid(In) → ADP + phosphate + phospholipid(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably involved in copper transport and in the regulation of cellular copper level
- Gene Name:
- PCA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38360
- Molecular weight:
- 131838.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Cu(2+)(In) → ADP + phosphate + Cu(2+)(Out). |
| ATP + H2O + Cd2+/in → ADP + phosphate + Cd2+/out |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of phospholipids (Potential). Leads to neomycin-resistance when overexpressed. Required for traffic between late Golgi and early endosomes
- Gene Name:
- NEO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40527
- Molecular weight:
- 130217.0
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phospholipid(In) → ADP + phosphate + phospholipid(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in DNA binding
- Specific function:
- Integrase (IN) targets the VLP to the nucleus, where a subparticle preintegration complex (PIC) containing at least integrase and the newly synthesized dsDNA copy of the retrotransposon must transit the nuclear membrane. Once in the nucleus, integrase performs the integration of the dsDNA into the host genome
- Gene Name:
- TY1B-OL
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12273
- Molecular weight:
- 198613.0
Reactions
| Deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) → diphosphate + DNA(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Exhibits ATP-dependent bile acid transport
- Gene Name:
- YBT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32386
- Molecular weight:
- 189160.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in the import of activated long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol to the peroxisomal matrix
- Gene Name:
- PXA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P34230
- Molecular weight:
- 97125.29688