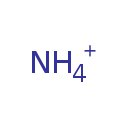
Ammonium (YMDB00423)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00423 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Ammonium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Ammonium ions are a waste product of the metabolism of animals. In fish and aquatic invertebrates, it is excreted directly into the water. In mammals, sharks, and amphibians, it is converted in the urea cycle to urea. In birds, reptiles, and terrestrial snails, metabolic ammonium is converted into uric acid, which is solid and can therefore be excreted with minimal water loss. Ammonium is an important source of nitrogen for many plant species, especially those growing on hypoxic soils. However, it is also toxic to most crop species and is rarely applied as a sole nitrogen source. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 14798-03-9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 18.0385 Monoisotopic: 18.034374133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/H3N/h1H3/p+1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | azanium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | azanium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | H4N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][N+]([H])([H])[H] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
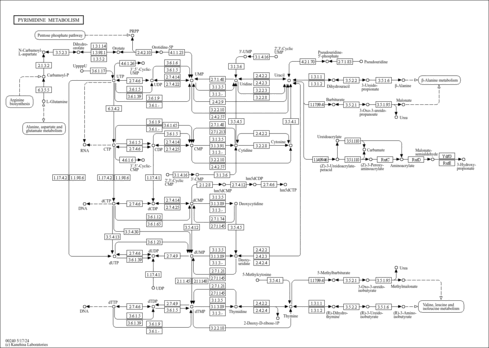
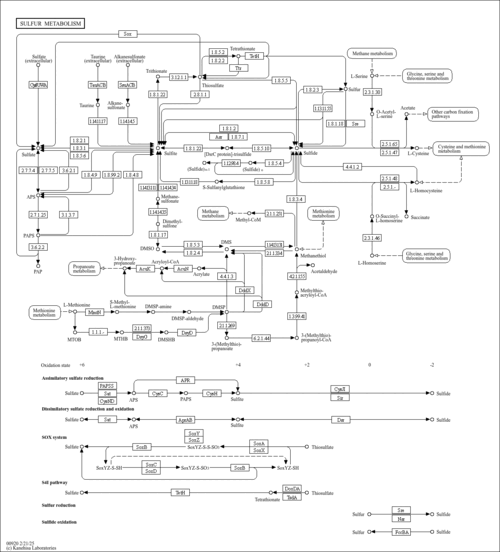
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Furnishes a means for formation of correctly charged Gln-tRNA(Gln) through the transamidation of misacylated Glu- tRNA(Gln) in the mitochondria. The reaction takes place in the presence of glutamine and ATP through an activated gamma-phospho- Glu-tRNA(Gln). Required for HMG2-induced ER-remodeling
- Gene Name:
- HER2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03557
- Molecular weight:
- 50918.0
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamyl-tRNA(Gln) + L-glutamine → ADP + phosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln) + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen
- Gene Name:
- URA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P28274
- Molecular weight:
- 64709.80078
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine
- Gene Name:
- GLN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32288
- Molecular weight:
- 41705.60156
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ASN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P49089
- Molecular weight:
- 64469.60156
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- ASN2
- Uniprot ID:
- P49090
- Molecular weight:
- 64592.5
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen. Plays an important role in the regulation of phospholipid synthesis
- Gene Name:
- URA8
- Uniprot ID:
- P38627
- Molecular weight:
- 63055.69922
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + deamido-NAD(+) + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + NAD(+) + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- QNS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38795
- Molecular weight:
- 80684.89844
Reactions
| ATP + deamido-NAD(+) + L-glutamine + H(2)O → AMP + diphosphate + NAD(+) + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of urea to ammonia and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- DUR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32528
- Molecular weight:
- 201830.0
Reactions
| ATP + urea + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + urea-1-carboxylate. |
| Urea-1-carboxylate + H(2)O → 2 CO(2) + 2 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase is a component of the alpha- ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. This includes the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). Acts also as component of the glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex), which catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- LPD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09624
- Molecular weight:
- 54009.69922
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine + NAD(+) → protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ureidoglycolate hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32459
- Molecular weight:
- 21726.59961
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + H(2)O → glyoxylate + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxamine-phosphate oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of either pyridoxine 5'- phosphate (PNP) or pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP) into pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)
- Gene Name:
- PDX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38075
- Molecular weight:
- 26908.0
Reactions
| Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate + H(2)O + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
| Pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine = L- cystathionine + succinate
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04533
- Molecular weight:
- 74312.70313
Reactions
| O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine → L-cystathionine + succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate
- Gene Name:
- CYS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P31373
- Molecular weight:
- 42541.69922
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- This enzyme scavenge exogenous and endogenous cytidine and 2'-deoxycytidine for UMP synthesis
- Gene Name:
- CDD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06549
- Molecular weight:
- 15535.90039
Reactions
| Cytidine + H(2)O → uridine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- AAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53909
- Molecular weight:
- 39634.69922
Reactions
| Adenosine + H(2)O → inosine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-threonine = 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ILV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00927
- Molecular weight:
- 63830.69922
Reactions
| L-threonine → 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- CHA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25379
- Molecular weight:
- 39301.0
Reactions
| L-serine → pyruvate + NH(3). |
| L-threonine → 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts cytosine to uracil or 5-methylcytosine to thymine by deaminating carbon number 4
- Gene Name:
- FCY1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12178
- Molecular weight:
- 17506.90039
Reactions
| Cytosine + H(2)O → uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the deamidation of nicotinamide, an early step in the NAD(+) salvage pathway. Positively regulates SIR2-mediated silencing and longevity by preventing the accumulation of intracellular nicotinamide, an inhibitor of SIR2, during times of stress. Acts also on nicotinyl hydroxamate
- Gene Name:
- PNC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53184
- Molecular weight:
- 24993.19922
Reactions
| Nicotinamide + H(2)O → nicotinate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- GDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P33327
- Molecular weight:
- 124331.0
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP3-1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11163
- Molecular weight:
- 38686.19922
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH3
- Uniprot ID:
- P39708
- Molecular weight:
- 49626.80078
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylbilane synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Tetrapolymerization of the monopyrrole PBG into the hydroxymethylbilane pre-uroporphyrinogen in several discrete steps
- Gene Name:
- HEM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28789
- Molecular weight:
- 36674.19922
Reactions
| 4 porphobilinogen + H(2)O → hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex) catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- GCV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P48015
- Molecular weight:
- 44468.69922
Reactions
| [Protein]-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + tetrahydrofolate → [protein]-dihydrolipoyllysine + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38986
- Molecular weight:
- 41394.80078
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07262
- Molecular weight:
- 49569.60156
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- STR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53101
- Molecular weight:
- 51828.0
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- AMP deaminase plays a critical role in energy metabolism
- Gene Name:
- AMD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15274
- Molecular weight:
- 93300.79688
Reactions
| AMP + H(2)O → IMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in riboflavin biosynthesis. Converts 2,5- diamino-6-(ribosylamino)-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate into 5- amino-6-(ribosylamino)-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione 5'-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- RIB2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12362
- Molecular weight:
- 67035.29688
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
| 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine + H(2)O → 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- IRC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P43623
- Molecular weight:
- 36971.10156
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Supplies the nucleotide substrate for thymidylate synthetase
- Gene Name:
- DCD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06773
- Molecular weight:
- 35645.69922
Reactions
| dCMP + H(2)O → dUMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of guanine, producing xanthine and ammonia
- Gene Name:
- GUD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07729
- Molecular weight:
- 55203.19922
Reactions
| Guanine + H(2)O → xanthine + NH(3). |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in ammonium transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transporter for ammonium (both charged and uncharged NH3 and NH4) to use as a nitrogen source. Can also transport methylamine. The affinity of MEP1 is about twenty times lower than that of MEP2. MEP3 has the lowest affinity
- Gene Name:
- MEP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40260
- Molecular weight:
- 54201.60156
- General function:
- Involved in ammonium transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transporter protein required for ammonia export. Induced in rho(0) cells, probably to eliminate the excess ammonia that arises because of a potential defect in ammonia assimilation in those cells
- Gene Name:
- ATO3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12359
- Molecular weight:
- 30028.09961
- General function:
- Involved in ammonium transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transporter for ammonium (both charged and uncharged NH3 and NH4) to use as a nitrogen source. The affinity of MEP2 is about twenty times higher than that of MEP1. MEP3 has the lowest affinity. Under ammonium limitation acts as an ammonium sensor, generating a signal that leads to pseudohyphal growth
- Gene Name:
- MEP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P41948
- Molecular weight:
- 53400.19922
- General function:
- Involved in ammonium transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transporter for ammonium (both charged and uncharged NH3 and NH4) to use as a nitrogen source. The affinity of MEP2 is about twenty times higher than that of MEP1. MEP3 has the lowest affinity
- Gene Name:
- MEP3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53390
- Molecular weight:
- 53689.39844