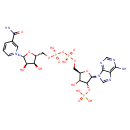
NADP (YMDB00427)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00427 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | NADP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | NADP, also known as NADP+ or TPN, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on NADP. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 53-59-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 744.4129 Monoisotopic: 744.083277073 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | XJLXINKUBYWONI-NNYOXOHSSA-O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H28N7O17P3/c22-17-12-19(25-7-24-17)28(8-26-12)21-16(44-46(33,34)35)14(30)11(43-21)6-41-48(38,39)45-47(36,37)40-5-10-13(29)15(31)20(42-10)27-3-1-2-9(4-27)18(23)32/h1-4,7-8,10-11,13-16,20-21,29-31H,5-6H2,(H7-,22,23,24,25,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39)/p+1/t10-,11-,13-,14-,15-,16-,20-,21-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-5-[({[({[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-3-carbamoyl-1lambda5-pyridin-1-ylium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-5-{[({[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]methyl}-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-3-carbamoyl-1lambda5-pyridin-1-ylium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C21H29N7O17P3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | NC(=O)C1=CC=C[N+](=C1)[C@@H]1O[C@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]2O[C@H]([C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H]2O)N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Simon, L. M.; Kotorman, M.; Szajani, B. Coenzyme production using immobilized enzymes. I. Preparation, characterization, and laboratory-scale application of an immobilized NAD+ kinase. Enzyme and Microbial Technology (1992), 14(12), 997-1000. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of D-arabinose, L-xylose, L- fucose and L-galactose in the presence of NADP+
- Gene Name:
- ARA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38115
- Molecular weight:
- 38883.19922
Reactions
| D-arabinose + NAD(P)(+) → D-arabinono-1,4-lactone + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes C14-demethylation of lanosterol which is critical for ergosterol biosynthesis. It transforms lanosterol into 4,4'-dimethyl cholesta-8,14,24-triene-3-beta-ol
- Gene Name:
- ERG11
- Uniprot ID:
- P10614
- Molecular weight:
- 60719.80078
Reactions
| Obtusifoliol + 3 O(2) + 3 NADPH → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-ergosta-8,14,24(28)-trien-3-beta-ol + formate + 3 NADP(+) + 4 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Unknown function which seems to be not essential
- Gene Name:
- GCY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P14065
- Molecular weight:
- 35078.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NADP(+) + H(2)O = L-glutamate + L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- LYS9
- Uniprot ID:
- P38999
- Molecular weight:
- 48917.30078
Reactions
| N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NADP(+) + H(2)O → L-glutamate + L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NADH
- Gene Name:
- ALD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P46367
- Molecular weight:
- 56723.19922
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- ALD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54114
- Molecular weight:
- 55384.80078
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = an acid + NADH
- Gene Name:
- ALD6
- Uniprot ID:
- P54115
- Molecular weight:
- 54413.69922
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Minor mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase isoform. Plays a role in regulation or biosynthesis of electron transport chain components. Involved in the biosynthesis of acetate during anaerobic growth on glucose
- Gene Name:
- ALD5
- Uniprot ID:
- P40047
- Molecular weight:
- 56620.39844
Reactions
| An aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADH. |
| An aldehyde + NADP(+) + H(2)O → an acid + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- May function in the production of NADPH for fatty acid and sterol synthesis
- Gene Name:
- IDP3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53982
- Molecular weight:
- 47856.0
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Mitochondrial IDP1 may regulate flux through the tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiration. Its probably critical function is the production of NADPH
- Gene Name:
- IDP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21954
- Molecular weight:
- 48189.89844
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- May function in the production of NADPH for fatty acid and sterol synthesis
- Gene Name:
- IDP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P41939
- Molecular weight:
- 46561.89844
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- The AROM polypeptide catalyzes 5 consecutive enzymatic reactions in prechorismate polyaromatic amino acid biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- ARO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08566
- Molecular weight:
- 174754.0
Reactions
| 3-deoxy-D-arabino-hept-2-ulosonate 7-phosphate → 3-dehydroquinate + phosphate. |
| 3-dehydroquinate → 3-dehydroshikimate + H(2)O. |
| Shikimate + NADP(+) → 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH. |
| ATP + shikimate → ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + 3-phosphoshikimate → phosphate + 5-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-3-phosphoshikimate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme catalyzes the second step in the common metabolic pathway to synthesize Thr and Met from Asp
- Gene Name:
- HOM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P13663
- Molecular weight:
- 39543.30078
Reactions
| L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + phosphate + NADP(+) → L-4-aspartyl phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the reduction of the keto group on the C-3 of sterols. Also facilitates the association of ERG7 with lipid particles preventing its digestion in the endoplasmic reticulum and the lipid particles
- Gene Name:
- ERG27
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12452
- Molecular weight:
- 39724.39844
Reactions
| 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NADP(+) → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-one + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of pyridoxal (PL) with NADPH and oxidation of pyridoxine (PN) with NADP(+)
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06494
- Molecular weight:
- 38600.39844
Reactions
| Pyridoxine + NADP(+) → pyridoxal + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP(+) = (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ILV5
- Uniprot ID:
- P06168
- Molecular weight:
- 44368.10156
Reactions
| (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP(+) → (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH. |
| (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate + NADP(+) → (S)-2-hydroxy-2-ethyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in synthesis of 1,3-beta-glucan. Could be a subunit of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase. Could be also a component of the membrane bound fatty acid elongation systems that produce the 26-carbon very long chain fatty acids that are precursors for ceramide and sphingolipids. Appears to be involved in the elongation of fatty acids up to 24 carbons. Appears to have the highest affinity for substrates with chain length less than 22 carbons
- Gene Name:
- FEN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25358
- Molecular weight:
- 40001.80078
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- This transmembrane glycoprotein is involved in the control of cholesterol biosynthesis. It is the rate-limiting enzyme of the sterol biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- HMG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P12683
- Molecular weight:
- 115624.0
Reactions
| (R)-mevalonate + CoA + 2 NADP(+) → (S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + 2 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- This transmembrane glycoprotein is involved in the control of cholesterol biosynthesis. It is the rate-limiting enzyme of the sterol biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- HMG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P12684
- Molecular weight:
- 115691.0
Reactions
| (R)-mevalonate + CoA + 2 NADP(+) → (S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + 2 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-CoA + O(2) = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2)
- Gene Name:
- POX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13711
- Molecular weight:
- 84041.39844
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + O(2) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- May be a membrane bound enzyme involved in the highly specific elongation of saturated 14-carbon fatty acids (14:0) to 16-carbon species (16:0)
- Gene Name:
- ELO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39540
- Molecular weight:
- 36233.60156
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Carrier of the growing fatty acid chain in fatty acid biosynthesis. May be involved in the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids. Accessory and non-catalytic subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), which functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain
- Gene Name:
- ACP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32463
- Molecular weight:
- 13942.5
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long- chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. The beta subunit contains domains for:[acyl-carrier-protein] acetyltransferase and malonyltransferase, S-acyl fatty acid synthase thioesterase, enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase, and 3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase
- Gene Name:
- FAS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07149
- Molecular weight:
- 228689.0
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADH + 2n NADPH → long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO(2) + 2n NAD(+) + 2n NADP(+). |
| Acetyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + acetyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| Malonyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| (3R)-3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → hexadec-2-enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O. |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH. |
| Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O → [acyl-carrier-protein] + oleate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long- chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. The alpha subunit contains domains for:acyl carrier protein, 3- oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase, and 3-oxoacyl-[acyl- carrier-protein] synthase. This subunit coordinates the binding of the six beta subunits to the enzyme complex
- Gene Name:
- FAS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P19097
- Molecular weight:
- 206945.0
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADH + 2n NADPH → long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO(2) + 2n NAD(+) + 2n NADP(+). |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetylglutamate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NADP(+) + phosphate = N-acetyl-5-glutamyl phosphate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ARG5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01217
- Molecular weight:
- 94868.39844
Reactions
| N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NADP(+) + phosphate → N-acetyl-5-glutamyl phosphate + NADPH. |
| ATP + N-acetyl-L-glutamate → ADP + N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Maintains high levels of reduced glutathione in the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- GLR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P41921
- Molecular weight:
- 53440.60156
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + NADP(+) → glutathione disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydrofolate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in folate metabolism. Catalyzes an essential reaction for de novo glycine and purine synthesis, and for DNA precursor synthesis
- Gene Name:
- DFR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07807
- Molecular weight:
- 24260.80078
Reactions
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) → 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase activity
- Specific function:
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- MIS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09440
- Molecular weight:
- 106216.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) → 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH. |
| 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O → 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
| ATP + formate + tetrahydrofolate → ADP + phosphate + 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase activity
- Specific function:
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ADE3
- Uniprot ID:
- P07245
- Molecular weight:
- 102204.0
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) → 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH. |
| 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O → 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
| ATP + formate + tetrahydrofolate → ADP + phosphate + 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in heme biosynthesis. Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of propionic acid side chains of rings A and B of coproporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- HEM13
- Uniprot ID:
- P11353
- Molecular weight:
- 37711.30078
Reactions
| Coproporphyrinogen-III + O(2) + 2 H(+) → protoporphyrinogen-IX + 2 CO(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Has several reductase activities that are NAD(P)H- dependent and involve FMN as a cofactor, ferricyanide being the best substrate for reduction. May be involved in ferric iron assimilation
- Gene Name:
- LOT6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07923
- Molecular weight:
- 21280.40039
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NAD(P)(+) → FMN + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH3
- Uniprot ID:
- P39708
- Molecular weight:
- 49626.80078
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07262
- Molecular weight:
- 49569.60156
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the activation of alpha-aminoadipate by ATP- dependent adenylation and the reduction of activated alpha- aminoadipate by NADPH
- Gene Name:
- LYS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07702
- Molecular weight:
- 155344.0
Reactions
| L-2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → L-2-aminoadipate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in monooxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) to form 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine (L-3OHKyn). Required for synthesis of quinolinic acid
- Gene Name:
- BNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P38169
- Molecular weight:
- 52428.89844
Reactions
| L-kynurenine + NADPH + O(2) → 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine + NADP(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Specifically phosphorylates NAD in the presence of ATP, dATP, or CTP as phosphoryl donors
- Gene Name:
- UTR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21373
- Molecular weight:
- 59468.69922
Reactions
| ATP + NAD(+) → ADP + NADP(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- HOM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P10869
- Molecular weight:
- 58109.19922
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate → ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the irreversible reduction of the cytotoxic compound methylglyoxal (MG) to (R)-lactaldehyde as an alternative to detoxification of MG by glyoxalase I GLO1. MG is synthesized via a bypath of glycolysis from dihydroxyacetone phosphate and is believed to play a role in cell cycle regulation and stress adaptation
- Gene Name:
- GRE2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12068
- Molecular weight:
- 38169.19922
Reactions
| Lactaldehyde + NADP(+) → methylglyoxal + NADPH. |
| 3-methylbutanol + NAD(P)+ → 3-methylbutanal + NAD(P)H + H+ |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates both NADH and NAD(+), with a twofold preference for NADH. Anti-oxidant factor and key source of the cellular reductant NADPH
- Gene Name:
- POS5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06892
- Molecular weight:
- 46246.5
Reactions
| ATP + NADH → ADP + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- MAE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36013
- Molecular weight:
- 74375.29688
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) → pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of precorrin-2 into siroheme. This reaction consist of the NAD-dependent oxidation of precorrin- 2 into sirohydrochlorin and its subsequent ferrochelation into siroheme
- Gene Name:
- MET8
- Uniprot ID:
- P15807
- Molecular weight:
- 31917.40039
Reactions
| Precorrin-2 + NAD(+) → sirohydrochlorin + NADH. |
| Siroheme + 2 H(+) → sirohydrochlorin + Fe(2+). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces the cytotoxic compound methylglyoxal (MG) to (R)-lactaldehyde similar to GRE2. MG is synthesized via a bypath of glycolysis from dihydroxyacetone phosphate and is believed to play a role in cell cycle regulation and stress adaptation. In pentose-fermenting yeasts, aldose reductase catalyzes the reduction of xylose into xylitol. The purified enzyme catalyzes this reaction, but the inability of S.cerevisiae to grow on xylose as sole carbon source indicates that the physiological function is more likely methylglyoxal reduction
- Gene Name:
- GRE3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38715
- Molecular weight:
- 37118.5
Reactions
| Alditol + NAD(P)(+) → aldose + NAD(P)H. |
| (R)-lactaldehyde + NADP(+) → methylglyoxal + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05016
- Molecular weight:
- 29158.09961
Reactions
| L-serine + NADP+ → 2-ammoniomalonate semialdehyde + NADPH + H+ |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of sulfite to sulfide, one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L-cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- ECM17
- Uniprot ID:
- P47169
- Molecular weight:
- 161218.0
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O → sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L-cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- MET10
- Uniprot ID:
- P39692
- Molecular weight:
- 114827.0
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O → sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- NADP-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase with a broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- ADH7
- Uniprot ID:
- P25377
- Molecular weight:
- 39348.19922
Reactions
| An alcohol + NADP(+) → an aldehyde + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in enzyme regulator activity
- Specific function:
- Required for calcium regulation. May regulate calcium accumulation by a non-vacuole organelle. Also regulates the activity of CSH1 and SUR1 during mannosyl phosphorylinositol ceramide synthesis
- Gene Name:
- CSG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P35206
- Molecular weight:
- 45441.60156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- NADP-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase with a broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- ADH6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04894
- Molecular weight:
- 39617.30078
Reactions
| An alcohol + NADP(+) → an aldehyde + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces benzil stereospecifically to (S)-benzoin. Is probably involved in a pathway contributing to genomic integrity
- Gene Name:
- IRC24
- Uniprot ID:
- P40580
- Molecular weight:
- 28803.90039
Reactions
| Benzoin + NADP(+) → benzil + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- PUT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07275
- Molecular weight:
- 64434.60156
Reactions
| (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O → L-glutamate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is suggested to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway
- Gene Name:
- ERG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32476
- Molecular weight:
- 55125.39844
Reactions
| Squalene + AH(2) + O(2) → (S)-squalene-2,3-epoxide + A + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-proline + NAD(P)(+) = 1-pyrroline-5- carboxylate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- PRO3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32263
- Molecular weight:
- 30131.59961
Reactions
| L-proline + NAD(P)(+) → 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH dependent reduction of L-gamma- glutamyl 5-phosphate into L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde and phosphate. The product spontaneously undergoes cyclization to form 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
- Gene Name:
- PRO2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54885
- Molecular weight:
- 49740.0
Reactions
| L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + phosphate + NADP(+) → L-glutamyl 5-phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-beta-hydroxy-delta5-steroid dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest- 7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) = 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha- cholest-7-en-3-one + CO(2) + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- ERG26
- Uniprot ID:
- P53199
- Molecular weight:
- 38706.10156
Reactions
| 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-one + CO(2) + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Prephenate + NADP(+) = 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- TYR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P20049
- Molecular weight:
- 50922.89844
Reactions
| Prephenate + NADP(+) → 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil reductase activity
- Specific function:
- 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribitylamino)uracil + NADP(+) = 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- RIB7
- Uniprot ID:
- P33312
- Molecular weight:
- 27116.0
Reactions
| 5-amino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribitylamino)uracil + NADP(+) → 5-amino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)uracil + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- NADPH + 2 quinone = NADP(+) + 2 semiquinone
- Gene Name:
- ZTA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38230
- Molecular weight:
- 37018.30078
Reactions
| NADPH + 2 quinone → NADP(+) + 2 semiquinone. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme with glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S- transferase (GST) activity. The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing cytosolic protein- and non-protein-disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Required for resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by directly reducing hydroperoxides and for the detoxification of ROS-mediated damage
- Gene Name:
- GRX2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17695
- Molecular weight:
- 15861.2998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Monothiol glutaredoxin involved in the biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters. Binds one iron-sulfur cluster per dimer. The iron-sulfur cluster is bound between subunits, and is complexed by a bound glutathione and a cysteine residue from each subunit (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- GRX4
- Uniprot ID:
- P32642
- Molecular weight:
- 27492.59961
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme with glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S- transferase (GST) activity. The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing cytosolic protein- and non-protein-disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Required for resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by directly reducing hydroperoxides and for the detoxification of ROS-mediated damage
- Gene Name:
- GRX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25373
- Molecular weight:
- 12380.09961
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first step in the removal of the two C-4 methyl groups of 4,4-dimethylzymosterol
- Gene Name:
- ERG25
- Uniprot ID:
- P53045
- Molecular weight:
- 36478.89844
Reactions
| 4,4-dimethyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
| 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O. |
| 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 3-ketodihydrosphingosine (KDS) to dihydrosphingosine (DHS)
- Gene Name:
- TSC10
- Uniprot ID:
- P38342
- Molecular weight:
- 35986.19922
Reactions
| Sphinganine + NADP(+) → 3-dehydrosphinganine + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Can convert acyl and alkyl dihydroxyacetone-phosphate (DHAP) into glycerolipids and ether lipids, respectively. Required for the biosynthesis of phosphatidic acid via the DHAP pathway, where it reduces 1-acyl DHAP to lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Required for spore germination
- Gene Name:
- AYR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P40471
- Molecular weight:
- 32813.60156
Reactions
| 1-palmitoylglycerol 3-phosphate + NADP(+) → palmitoylglycerone phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Metalloreductase responsible for reducing extracellular iron and copper prior to import. Catalyzes the reductive uptake of Fe(3+)-salts and Fe(3+) bound to catecholate or hydroxamate siderophores. Fe(3+) is reduced to Fe(2+), which then dissociates from the siderophore and can be imported by the high-affinity Fe(2+) transport complex in the plasma membrane. Also participates in Cu(2+) reduction and Cu(+) uptake
- Gene Name:
- FRE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32791
- Molecular weight:
- 78853.0
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Siderophore-iron reductase responsible for reducing extracellular iron prior to import. Catalyzes the reductive uptake of Fe(3+) bound to dihydroxamate rhodotorulic acid. Fe(3+) is reduced to Fe(2+), which then dissociates from the siderophore and can be imported by the high-affinity Fe(2+) transport complex in the plasma membrane
- Gene Name:
- FRE4
- Uniprot ID:
- P53746
- Molecular weight:
- 82014.60156
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Siderophore-iron reductase responsible for reducing extracellular iron prior to import. Catalyzes the reductive uptake of Fe(3+) bound to di- and trihydroxamate siderophores. Fe(3+) is reduced to Fe(2+), which then dissociates from the siderophore and can be imported by the high-affinity Fe(2+) transport complex in the plasma membrane
- Gene Name:
- FRE3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08905
- Molecular weight:
- 80588.5
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Cell surface metalloreductase
- Gene Name:
- FRE5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08908
- Molecular weight:
- 80291.70313
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Metalloreductase responsible for reducing vacuolar iron and copper prior to transport into the cytosol. Catalyzes the reduction of Fe(3+) to Fe(2+) and Cu(2+) to Cu(+), respectively, which can then be transported by the respective vacuolar efflux systems to the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- FRE6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12473
- Molecular weight:
- 81988.29688
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Metalloreductase responsible for reducing extracellular iron and copper prior to import. Catalyzes the reductive uptake of Fe(3+)-salts and Fe(3+) bound to catecholate or hydroxamate siderophores. Fe(3+) is reduced to Fe(2+), which then dissociates from the siderophore and can be imported by the high-affinity Fe(2+) transport complex in the plasma membrane. Also participates in Cu(2+) reduction and Cu(+) uptake
- Gene Name:
- FRE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P36033
- Molecular weight:
- 80071.5
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates as a hydrogen donor in redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. It is involved in many cellular processes, including deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, repair of oxidatively damaged proteins, protein folding, sulfur metabolism, and redox homeostasis. Thioredoxin-dependent enzymes include phosphoadenosine-phosphosulfate reductase MET16, alkyl- hydroperoxide reductase DOT5, thioredoxin peroxidases TSA1 and TSA2, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase AHP1, and peroxiredoxin HYR1. Thioredoxin is also involved in protection against reducing stress. As part of the LMA1 complex, it is involved in the facilitation of vesicle fusion such as homotypic vacuole and ER- derived COPII vesicle fusion with the Golgi. This activity does not require the redox mechanism. Through its capacity to inactivate the stress response transcription factor YAP1 and its regulator the hydroperoxide stress sensor HYR1, it is involved in feedback regulation of stress response gene expression upon oxidative stress
- Gene Name:
- TRX2
- Uniprot ID:
- P22803
- Molecular weight:
- 11203.7998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates as a hydrogen donor in redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. It is involved in many cellular processes, including deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, repair of oxidatively damaged proteins, protein folding, sulfur metabolism, and redox homeostasis. Thioredoxin-dependent enzymes include phosphoadenosine-phosphosulfate reductase MET16, alkyl- hydroperoxide reductase DOT5, thioredoxin peroxidases TSA1 and TSA2, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase AHP1, and peroxiredoxin HYR1. Thioredoxin is also involved in protection against reducing stress. As part of the LMA1 complex, it is involved in the facilitation of vesicle fusion such as homotypic vacuole and ER- derived COPII vesicle fusion with the Golgi. This activity does not require the redox mechanism
- Gene Name:
- TRX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22217
- Molecular weight:
- 11234.90039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6- phosphogluconate to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO(2), with concomitant reduction of NADP to NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GND1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38720
- Molecular weight:
- 53542.69922
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate + NADP(+) → D-ribulose 5-phosphate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6- phosphogluconate to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO(2), with concomitant reduction of NADP to NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GND2
- Uniprot ID:
- P53319
- Molecular weight:
- 53922.30078
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate + NADP(+) → D-ribulose 5-phosphate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- May regulate the flux of isoprene intermediates through the sterol pathway. Squalene synthase is crucial for balancing the incorporation of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) into sterol and nonsterol isoprene synthesis. ERG9 is also essential for cell growth in yeast
- Gene Name:
- ERG9
- Uniprot ID:
- P29704
- Molecular weight:
- 51719.39844
Reactions
| 2 farnesyl diphosphate → diphosphate + presqualene diphosphate. |
| Presqualene diphosphate + NAD(P)H → squalene + diphosphate + NAD(P)(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- UGA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38067
- Molecular weight:
- 54188.80078
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O → succinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in delta14-sterol reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces the C14=C15 double bond of 4,4-dimethyl- cholesta-8,14,24-trienol to produce 4,4-dimethyl-cholesta-8,24- dienol
- Gene Name:
- ERG24
- Uniprot ID:
- P32462
- Molecular weight:
- 50615.0
Reactions
| 4,4-dimethyl-5-alpha-cholesta-8,24-dien-3-beta-ol + NADP(+) → 4,4-dimethyl-5-alpha-cholesta-8,14,24-trien-3-beta-ol + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- YPR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12458
- Molecular weight:
- 34754.69922
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Required for hydroxylation of C-4 in the sphingoid moiety of ceramide. Involved in the response to syringomycin
- Gene Name:
- SUR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38992
- Molecular weight:
- 40734.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Required for respiration and the maintenance of the mitochondrial compartment. May have a role in the mitochondrial synthesis of fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- ETR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38071
- Molecular weight:
- 42066.5
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH. |
| Acyl-CoA + NADP(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- 2 reduced ferredoxin + NADP(+) + H(+) = 2 oxidized ferredoxin + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ARH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P48360
- Molecular weight:
- 56236.69922
Reactions
| 2 reduced ferredoxin + NADP(+) + H(+) → 2 oxidized ferredoxin + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
- Specific function:
- Component of the microsomal membrane bound fatty acid elongation system, which produces the 26-carbon very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) from palmitate. Catalyzes the last step in each elongation cycle that lengthens palmitate by two carbon units. VLCFAs serve as precursors for ceramide and sphingolipids. Required for normal biogenesis of piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus (PMN) bleps and vesicles during nutrient stress
- Gene Name:
- TSC13
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99190
- Molecular weight:
- 36767.5
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + NADP(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids in mitochondria
- Gene Name:
- OAR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35731
- Molecular weight:
- 31183.69922
Reactions
| (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes beta-NADH, beta-NADPH, and alpha-NADPH
- Gene Name:
- OYE2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03558
- Molecular weight:
- 45010.39844
Reactions
| NADPH + acceptor → NADP(+) + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Auxiliary enzyme of beta-oxidation. Participates in the degradation of unsaturated fatty enoyl-CoA esters having double bonds in both even- and odd-numbered positions in peroxisome. Catalyzes the NADP-dependent reduction of 2,4-dienoyl-CoA to yield trans-3-enoyl-CoA. Dispensable for growth and sporulation on solid acetate and oleate media, but is essential for these processes to occur on petroselineate
- Gene Name:
- SPS19
- Uniprot ID:
- P32573
- Molecular weight:
- 31108.69922
Reactions
| Trans-2,3-didehydroacyl-CoA + NADP(+) → trans,trans-2,3,4,5-tetradehydroacyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the microsomal membrane bound fatty acid elongation system, which produces the 26-carbon very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) from palmitate. Catalyzes the reduction of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA intermediate that is formed in each cycle of fatty acid elongation. VLCFAs serve as precursors for ceramide and sphingolipids
- Gene Name:
- IFA38
- Uniprot ID:
- P38286
- Molecular weight:
- 38707.80078
Reactions
| 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NADP(+) → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes beta-NADH, beta-NADPH, and alpha-NADPH
- Gene Name:
- OYE3
- Uniprot ID:
- P41816
- Molecular weight:
- 44920.10156
Reactions
| NADPH + acceptor → NADP(+) + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme is required for electron transfer from NADP to cytochrome P450 in microsomes. It can also provide electron transfer to heme oxygenase and cytochrome B5
- Gene Name:
- NCP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16603
- Molecular weight:
- 76771.10156
Reactions
| NADPH + n oxidized hemoprotein → NADP(+) + n reduced hemoprotein. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on thioredoxins 1 and 2
- Gene Name:
- TRR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P29509
- Molecular weight:
- 34237.80078
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) → thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on mitochondrial thioredoxin 3. Implicated in the defense against oxidative stress
- Gene Name:
- TRR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38816
- Molecular weight:
- 37087.0
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) → thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in delta24(24-1) sterol reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Ergosterol + NADP(+) = ergosta- 5,7,22,24(24(1))-tetraen-3-beta-ol + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ERG4
- Uniprot ID:
- P25340
- Molecular weight:
- 56039.30078
Reactions
| Ergosterol + NADP(+) → ergosta-5,7,22,24(24(1))-tetraen-3-beta-ol + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilizes O(2) and electrons from the reduced cytochrome b(5) domain to catalyze the insertion of a double bond into a spectrum of fatty acyl-CoA substrates (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- OLE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21147
- Molecular weight:
- 58402.60156
Reactions
| Stearoyl-CoA + 2 ferrocytochrome b5 + O(2) + 2 H(+) → oleoyl-CoA + 2 ferricytochrome b5 + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Ceramide hydroxylase involved in the alpha-hydroxylation of sphingolipid-associated very long chain fatty acids. Hydroxylates the very long chain fatty acid of ceramides at C2 and C3
- Gene Name:
- SCS7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03529
- Molecular weight:
- 44881.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the introduction of a C-5 double bond in the B ring of ergosterol. May contribute to the regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- ERG3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32353
- Molecular weight:
- 42729.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TRX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P25372
- Molecular weight:
- 14432.0
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P53839
- Molecular weight:
- 38831.19922
Reactions
| glycolate + NADP+ → glyoxylate + NADPH + H+. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- HOM6
- Uniprot ID:
- P31116
- Molecular weight:
- 38501.69922
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) → L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- D-glucose 6-phosphate + NADP(+) = D-glucono- 1,5-lactone 6-phosphate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ZWF1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11412
- Molecular weight:
- 57521.10156
Reactions
| D-glucose 6-phosphate + NADP(+) → 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of ketopantoate into pantoic acid
- Gene Name:
- PAN5
- Uniprot ID:
- P38787
- Molecular weight:
- 42820.89844
Reactions
| (R)-pantoate + NADP(+) → 2-dehydropantoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) = 5,10- methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- MET13
- Uniprot ID:
- P53128
- Molecular weight:
- 68559.5
Reactions
| 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) → 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Cell surface metalloreductase. May be involved in copper homeostasis
- Gene Name:
- FRE7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12333
- Molecular weight:
- 70904.70313
Reactions
| 2 Fe(2+) + NADP(+) → 2 Fe(3+) + NADPH. |