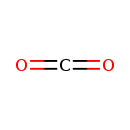
Carbon dioxide (YMDB00912)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00912 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Carbon dioxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced during respiration by all animals, fungi and microorganisms. Traditionally, the carbonation in beer and sparkling wine comes about through natural fermentation of carbohydrates, but some manufacturers carbonate these drinks artificially. The production of CO2 by yeast breaking down carbohydrates is the reason bread rises. Gluten chains in the bread hold the carbon dioxide in creating the airiness of the bread. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 124-38-9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 44.0095 Monoisotopic: 43.989829244 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/CO2/c2-1-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | methanedione | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | carbon dioxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | CO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | O=C=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal oxides. These are inorganic compounds containing an oxygen atom of an oxidation state of -2, in which the heaviest atom bonded to the oxygen belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Other non-metal organides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Other non-metal oxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Other non-metal oxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Gas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | -56.5 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Callahan, Richard A. Process and apparatus for producing liquid carbon dioxide. U.S. (1993), 11 pp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- TRP3
- Uniprot ID:
- P00937
- Molecular weight:
- 53488.89844
Reactions
| Chorismate + L-glutamine → anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate. |
| 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate → 1-C-(3-indolyl)-glycerol 3-phosphate + CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of urea to ammonia and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- DUR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32528
- Molecular weight:
- 201830.0
Reactions
| ATP + urea + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + urea-1-carboxylate. |
| Urea-1-carboxylate + H(2)O → 2 CO(2) + 2 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex) catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The P protein binds the alpha-amino group of glycine through its pyridoxal phosphate cofactor; CO(2) is released and the remaining methylamine moiety is then transferred to the lipoamide cofactor of the H protein
- Gene Name:
- GCV2
- Uniprot ID:
- P49095
- Molecular weight:
- 114450.0
Reactions
| Glycine + H-protein-lipoyllysine → H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in 5-aminolevulinate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Succinyl-CoA + glycine = 5-aminolevulinate + CoA + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- HEM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09950
- Molecular weight:
- 59361.69922
Reactions
| Succinyl-CoA + glycine → 5-aminolevulinate + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase is a component of the alpha- ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. This includes the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). Acts also as component of the glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex), which catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- LPD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09624
- Molecular weight:
- 54009.69922
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine + NAD(+) → protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Second most abundant of three pyruvate decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6) implicated in the nonoxidative conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide during alcoholic fermentation. Most of the produced acetaldehyde is subsequently reduced to ethanol, but some is required for cytosolic acetyl-CoA production for biosynthetic pathways. The enzyme is also one of five 2-oxo acid decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ARO10, and THI3) able to decarboxylate more complex 2-oxo acids (alpha-keto-acids) than pyruvate, which seem mainly involved in amino acid catabolism. Here the enzyme catalyzes the decarboxylation of amino acids, which, in a first step, have been transaminated to the corresponding 2-oxo acids. In a third step, the resulting aldehydes are reduced to alcohols, collectively referred to as fusel oils or alcohols. Its preferred substrates are the transaminated amino acids valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, whereas leucine is no substrate. In a side-reaction the carbanionic intermediate (or active aldehyde) generated by decarboxylation or by activation of an aldehyde can react with an aldehyde via condensation (or carboligation) yielding a 2-hydroxy ketone, collectively called acyloins
- Gene Name:
- PDC5
- Uniprot ID:
- P16467
- Molecular weight:
- 61911.60156
Reactions
| A 2-oxo acid → an aldehyde + CO(2). |
| 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvate → 2-(indol-3-yl)acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Phenylpyruvate → phenylacetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Pyruvate → Acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| A 2-oxo acid + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone + CO(2). |
| An aldehyde + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Minor of three pyruvate decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6) implicated in the nonoxidative conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide during alcoholic fermentation. Most of the produced acetaldehyde is subsequently reduced to ethanol, but some is required for cytosolic acetyl-CoA production for biosynthetic pathways. The enzyme is also one of five 2-oxo acid decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ARO10, and THI3) able to decarboxylate more complex 2-oxo acids (alpha-keto-acids) than pyruvate, which seem mainly involved in amino acid catabolism. Here the enzyme catalyzes the decarboxylation of amino acids, which, in a first step, have been transaminated to the corresponding 2-oxo acids. In a third step, the resulting aldehydes are reduced to alcohols, collectively referred to as fusel oils or alcohols. Its preferred substrates are the transaminated amino acids valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, whereas leucine is no substrate. In a side-reaction the carbanionic intermediate (or active aldehyde) generated by decarboxylation or by activation of an aldehyde can react with an aldehyde via condensation (or carboligation) yielding a 2-hydroxy ketone, collectively called acyloins. The expression level of this protein in the presence of fermentable carbon sources is so low that it can not compensate for the other two pyruvate decarboxylases to sustain fermentation
- Gene Name:
- PDC6
- Uniprot ID:
- P26263
- Molecular weight:
- 61579.89844
Reactions
| A 2-oxo acid → an aldehyde + CO(2). |
| 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvate → 2-(indol-3-yl)acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Phenylpyruvate → phenylacetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Pyruvate → Acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| A 2-oxo acid + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone + CO(2). |
| An aldehyde + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Major of three pyruvate decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6) implicated in the nonoxidative conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide during alcoholic fermentation. Most of the produced acetaldehyde is subsequently reduced to ethanol, but some is required for cytosolic acetyl-CoA production for biosynthetic pathways. The enzyme is also one of five 2-oxo acid decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ARO10, and THI3) able to decarboxylate more complex 2-oxo acids (alpha-ketoacids) than pyruvate, which seem mainly involved in amino acid catabolism. Here the enzyme catalyzes the decarboxylation of amino acids, which, in a first step, have been transaminated to the corresponding 2-oxo acids. In a third step, the resulting aldehydes are reduced to alcohols, collectively referred to as fusel oils or alcohols. Its preferred substrates are the transaminated amino acids valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, whereas leucine is no substrate. In a side-reaction the carbanionic intermediate (or active aldehyde) generated by decarboxylation or by activation of an aldehyde can react with an aldehyde via condensation (or carboligation) yielding a 2-hydroxy ketone, collectively called acyloins
- Gene Name:
- PDC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06169
- Molecular weight:
- 61494.89844
Reactions
| A 2-oxo acid → an aldehyde + CO(2). |
| 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvate → 2-(indol-3-yl)acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Phenylpyruvate → phenylacetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| Pyruvate → Acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| A 2-oxo acid + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone + CO(2). |
| An aldehyde + an aldehyde → A 2-hydroxy ketone. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Orotidine 5'-phosphate = UMP + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- URA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P03962
- Molecular weight:
- 29239.30078
Reactions
| Orotidine 5'-phosphate → UMP + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Performs an essential role in the oxidative function of the citric acid cycle. Also binds RNA; specifically to the 5'- untranslated leaders of mitochondrial mRNAs
- Gene Name:
- IDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P28834
- Molecular weight:
- 39323.69922
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NAD(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Performs an essential role in the oxidative function of the citric acid cycle. Also binds RNA; specifically to the 5'- untranslated leaders of mitochondrial mRNAs
- Gene Name:
- IDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P28241
- Molecular weight:
- 39739.0
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NAD(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- May function in the production of NADPH for fatty acid and sterol synthesis
- Gene Name:
- IDP3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53982
- Molecular weight:
- 47856.0
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Mitochondrial IDP1 may regulate flux through the tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiration. Its probably critical function is the production of NADPH
- Gene Name:
- IDP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21954
- Molecular weight:
- 48189.89844
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- May function in the production of NADPH for fatty acid and sterol synthesis
- Gene Name:
- IDP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P41939
- Molecular weight:
- 46561.89844
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
| Oxalosuccinate + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ureidoglycolate hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32459
- Molecular weight:
- 21726.59961
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + H(2)O → glyoxylate + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first reaction in the catabolism of the essential branched chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Involved in cell cycle regulation
- Gene Name:
- BAT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P47176
- Molecular weight:
- 41624.39844
Reactions
| L-leucine + 2-oxoglutarate → 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + L-glutamate. |
| 2-oxoglutaric acid + L-isoleucine → (S)-3-methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid + L-glutamic acid. |
| 2-oxoglutaric acid + L-valine → 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid + L-glutamic acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first reaction in the catabolism of the essential branched chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Appears to be involved in the regulation of the transition from G1 to S phase in the cell cycle. High copy suppressor of a temperature-sensitive mutation in the ABC transporter, ATM1
- Gene Name:
- BAT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38891
- Molecular weight:
- 43595.69922
Reactions
| L-leucine + 2-oxoglutarate → 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + L-glutamate. |
| 2-oxoglutaric acid + L-isoleucine → (S)-3-methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid + L-glutamic acid. |
| 2-oxoglutaric acid + L-valine → 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid + L-glutamic acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in synthesis of 1,3-beta-glucan. Could be a subunit of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase. Could be also a component of the membrane bound fatty acid elongation systems that produce the 26-carbon very long chain fatty acids that are precursors for ceramide and sphingolipids. Appears to be involved in the elongation of fatty acids up to 24 carbons. Appears to have the highest affinity for substrates with chain length less than 22 carbons
- Gene Name:
- FEN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25358
- Molecular weight:
- 40001.80078
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring nitrogenous groups
- Specific function:
- Component of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), which catalyzes the committed step in the synthesis of sphingolipids, the condensation of serine with palmitoyl CoA to form the long chain base 3-ketosphinganine
- Gene Name:
- LCB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25045
- Molecular weight:
- 62206.60156
Reactions
| Palmitoyl-CoA + L-serine → CoA + 3-dehydro-D-sphinganine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- May be a membrane bound enzyme involved in the highly specific elongation of saturated 14-carbon fatty acids (14:0) to 16-carbon species (16:0)
- Gene Name:
- ELO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39540
- Molecular weight:
- 36233.60156
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Carrier of the growing fatty acid chain in fatty acid biosynthesis. May be involved in the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids. Accessory and non-catalytic subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), which functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain
- Gene Name:
- ACP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32463
- Molecular weight:
- 13942.5
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long- chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. The beta subunit contains domains for:[acyl-carrier-protein] acetyltransferase and malonyltransferase, S-acyl fatty acid synthase thioesterase, enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase, and 3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase
- Gene Name:
- FAS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07149
- Molecular weight:
- 228689.0
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADH + 2n NADPH → long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO(2) + 2n NAD(+) + 2n NADP(+). |
| Acetyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + acetyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| Malonyl-CoA + [acyl-carrier-protein] → CoA + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| (3R)-3-hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → hexadec-2-enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O. |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH. |
| Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O → [acyl-carrier-protein] + oleate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long- chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. The alpha subunit contains domains for:acyl carrier protein, 3- oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase, and 3-oxoacyl-[acyl- carrier-protein] synthase. This subunit coordinates the binding of the six beta subunits to the enzyme complex
- Gene Name:
- FAS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P19097
- Molecular weight:
- 206945.0
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADH + 2n NADPH → long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO(2) + 2n NAD(+) + 2n NADP(+). |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
| (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalytic subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), which catalyzes the committed step in the synthesis of sphingolipids, the condensation of serine with palmitoyl CoA to form the long chain base 3-ketosphinganine
- Gene Name:
- LCB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P40970
- Molecular weight:
- 63110.19922
Reactions
| Palmitoyl-CoA + L-serine → CoA + 3-dehydro-D-sphinganine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PDA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P12695
- Molecular weight:
- 51817.5
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine → CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-acetyldihydrolipoyl)lysine. |
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P40506
- Molecular weight:
- 41892.69922
Reactions
| CTP + (R)-4'-phosphopantothenate + L-cysteine → CMP + PPi + N-((R)-4'-phosphopantothenoyl)-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Maintains high levels of reduced glutathione in the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- GLR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P41921
- Molecular weight:
- 53440.60156
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + NADP(+) → glutathione disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4- carboxylate = 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ADE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P21264
- Molecular weight:
- 62338.69922
Reactions
| 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate → 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin
- Gene Name:
- BIO4
- Uniprot ID:
- P53630
- Molecular weight:
- 26256.69922
Reactions
| ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) → ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the catabolism of quinolinic acid (QA)
- Gene Name:
- BNA6
- Uniprot ID:
- P43619
- Molecular weight:
- 32364.69922
Reactions
| Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate + CO(2) → pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in heme biosynthesis. Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of propionic acid side chains of rings A and B of coproporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- HEM13
- Uniprot ID:
- P11353
- Molecular weight:
- 37711.30078
Reactions
| Coproporphyrinogen-III + O(2) + 2 H(+) → protoporphyrinogen-IX + 2 CO(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of four acetate groups of uroporphyrinogen-III to yield coproporphyrinogen-III
- Gene Name:
- HEM12
- Uniprot ID:
- P32347
- Molecular weight:
- 41348.69922
Reactions
| Uroporphyrinogen III → coproporphyrinogen + 4 CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the rate-limiting reaction in the mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (FAS) type II pathway. Responsible for the production of the mitochondrial malonyl-CoA, used for the biosynthesis of the cofactor lipoic acid. This protein carries three functions:biotin carboxyl carrier protein, biotin carboxylase, and carboxyltransferase
- Gene Name:
- HFA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32874
- Molecular weight:
- 259161.0
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
| ATP + biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) → ADP + phosphate + carboxy-biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-5-diphosphomevalonate = ADP + phosphate + isopentenyl diphosphate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- MVD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32377
- Molecular weight:
- 44115.5
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-5-diphosphomevalonate → ADP + phosphate + isopentenyl diphosphate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Carries out three functions:biotin carboxyl carrier protein, biotin carboxylase and carboxyltransferase
- Gene Name:
- FAS3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q00955
- Molecular weight:
- 250351.0
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
| ATP + biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) → ADP + phosphate + carboxy-biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + oxaloacetate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PCK1
- Uniprot ID:
- P10963
- Molecular weight:
- 60982.69922
Reactions
| ATP + oxaloacetate → ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- MAE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36013
- Molecular weight:
- 74375.29688
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) → pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- FDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08911
- Molecular weight:
- 41714.0
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) → CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- FDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P0CF35
- Molecular weight:
- 26487.19922
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) → CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(+)-dependent conversion of homoisocitrate to alpha-ketoadipate
- Gene Name:
- LYS12
- Uniprot ID:
- P40495
- Molecular weight:
- 40068.60156
Reactions
| (1R,2S)-1-hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylate + NAD(+) → 2-oxoadipate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-4- methylpentanoate (3-isopropylmalate) to 3-carboxy-4-methyl-2- oxopentanoate. The product decarboxylates to 4-methyl-2 oxopentanoate
- Gene Name:
- LEU2
- Uniprot ID:
- P04173
- Molecular weight:
- 38952.5
Reactions
| (2R,3S)-3-isopropylmalate + NAD(+) → 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts as a alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase active on sulfonates. Although taurine is a poor substrate, a variety of other sulfonates are utilized, with the best natural substrates being isethionate and taurocholate
- Gene Name:
- JLP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12358
- Molecular weight:
- 46982.30078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- One of five 2-oxo acid decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ARO10, and THI3) involved in amino acid catabolism. The enzyme catalyzes the decarboxylation of amino acids, which, in a first step, have been transaminated to the corresponding 2-oxo acids (alpha-keto-acids). In a third step, the resulting aldehydes are reduced to alcohols, collectively referred to as fusel oils or alcohols. Its preferred substrates are the transaminated amino acids, phenylalanine, tryptophan, (and probably tyrosine), but also isoleucine, whereas leucine is a low efficiency and valine and pyruvate are no substrates. In analogy to the pyruvate decarboxylases the enzyme may in a side-reaction catalyze condensation (or carboligation) reactions leading to the formation of 2-hydroxy ketone, collectively called acyloins
- Gene Name:
- ARO10
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06408
- Molecular weight:
- 71383.79688
Reactions
| A 2-oxo acid → an aldehyde + CO(2). |
| Phenylpyruvate → phenylacetaldehyde + CO(2). |
| 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvate → 2-(indol-3-yl)acetaldehyde + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in adenosylmethionine decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase is essential for normal growth, sporulation, maintenance of ds-RNA virus, biosynthesis of spermine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- SPE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P21182
- Molecular weight:
- 46232.0
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine → (5-deoxy-5-adenosyl)(3-aminopropyl)-methylsulfonium salt + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-ornithine = putrescine + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- SPE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08432
- Molecular weight:
- 52284.80078
Reactions
| L-ornithine → putrescine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-beta-hydroxy-delta5-steroid dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest- 7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) = 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha- cholest-7-en-3-one + CO(2) + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- ERG26
- Uniprot ID:
- P53199
- Molecular weight:
- 38706.10156
Reactions
| 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-one + CO(2) + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Prephenate + NADP(+) = 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- TYR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P20049
- Molecular weight:
- 50922.89844
Reactions
| Prephenate + NADP(+) → 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (succinyl-transferring) activity
- Specific function:
- The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- KGD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P20967
- Molecular weight:
- 114416.0
Reactions
| 2-oxoglutarate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] lipoyllysine → [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] S-succinyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, disulfide as acceptor
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PDA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16387
- Molecular weight:
- 46342.69922
Reactions
| Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine → [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PDB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32473
- Molecular weight:
- 40053.19922
Reactions
| Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine → [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ILV2
- Uniprot ID:
- P07342
- Molecular weight:
- 74936.29688
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate → 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6- phosphogluconate to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO(2), with concomitant reduction of NADP to NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GND1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38720
- Molecular weight:
- 53542.69922
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate + NADP(+) → D-ribulose 5-phosphate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6- phosphogluconate to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO(2), with concomitant reduction of NADP to NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GND2
- Uniprot ID:
- P53319
- Molecular weight:
- 53922.30078
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate + NADP(+) → D-ribulose 5-phosphate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate = 4-aminobutanoate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- GAD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04792
- Molecular weight:
- 65989.5
Reactions
| L-glutamate → 4-aminobutanoate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- One of five 2-oxo acid decarboxylases (PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ARO10, and THI3) involved in amino acid catabolism. The enzyme catalyzes the decarboxylation of amino acids, which, in a first step, have been transaminated to the corresponding 2-oxo acids (alpha-keto-acids). In a third step, the resulting aldehydes are reduced to alcohols, collectively referred to as fusel oils or alcohols. Its preferred substrates are the transaminated amino acids leucine and isoleucine, whereas valine, aromatic amino acids, and pyruvate are no substrates. In analogy to the pyruvate decarboxylases the enzyme may in a side-reaction catalyze condensation (or carboligation) reactions leading to the formation of 2-hydroxy ketone, collectively called acyloins. The enzyme is also positively regulating the thiamine metabolism by a molecular mechanism that may involve thiamine concentration sensing and signal transmission
- Gene Name:
- THI3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07471
- Molecular weight:
- 68365.79688
Reactions
| A 2-oxo acid → an aldehyde + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in carbonate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO(2) to H(2)CO(3). The main role may be to provide inorganic carbon for the bicarbonate-dependent carboxylation reactions catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and carbamoyl- phosphate synthetase. Involved in protection against oxidative damage. Encodes a substrate for the non-classical protein export pathway for proteins that lack a cleavable signal sequence
- Gene Name:
- NCE103
- Uniprot ID:
- P53615
- Molecular weight:
- 24859.0
Reactions
| H(2)CO(3) → CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- May be involved in the regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis and interorganelle trafficking of phosphatidylserine
- Gene Name:
- PSD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39006
- Molecular weight:
- 56594.39844
Reactions
| Phosphatidyl-L-serine → phosphatidylethanolamine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Possibly involved in the synthesis of a specialized molecule, probably related to a fatty acid, which is essential for mitochondrial respiration. Is essential for oxygen uptake and the presence of cytochromes A and B
- Gene Name:
- CEM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39525
- Molecular weight:
- 47554.69922
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] → 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- May be involved in the regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis and interorganelle trafficking of phosphatidylserine
- Gene Name:
- PSD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P53037
- Molecular weight:
- 130064.0
Reactions
| Phosphatidyl-L-serine → phosphatidylethanolamine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in prephenate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Prephenate = phenylpyruvate + H(2)O + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- PHA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P32452
- Molecular weight:
- 38224.80078
Reactions
| Prephenate → phenylpyruvate + H(2)O + CO(2). |
- General function:
- ferulate metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible decarboxylation of aromatic carboxylic acids like ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid or cinnamic acid, producing the corresponding vinyl derivatives 4-vinylphenol, 4-vinylguaiacol, and styrene, respectively, which play the role of aroma metabolites (PubMed:20471595, PubMed:25647642). Not essential for ubiquinone synthesis (PubMed:20471595).
- Gene Name:
- FDC1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03034
- Molecular weight:
- 56163.39