oxygen (YMDB00900)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00900 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | oxygen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Oxygen, also known as dioxygene or O2, belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal oxides. These are inorganic compounds containing an oxygen atom of an oxidation state of -2, in which the heaviest atom bonded to the oxygen belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. Oxygen is possibly neutral. Oxygen exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 7782-44-7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 31.9988 Monoisotopic: 31.989829244 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/O2/c1-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | dioxygen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | singlet oxygen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | O=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal oxides. These are inorganic compounds containing an oxygen atom of an oxidation state of -2, in which the heaviest atom bonded to the oxygen belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Other non-metal organides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Other non-metal oxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Other non-metal oxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | -218.4 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
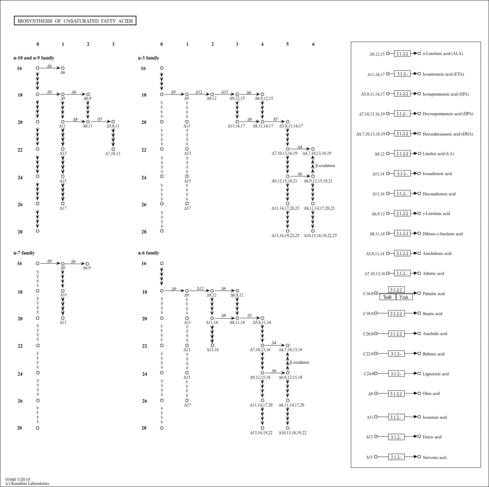
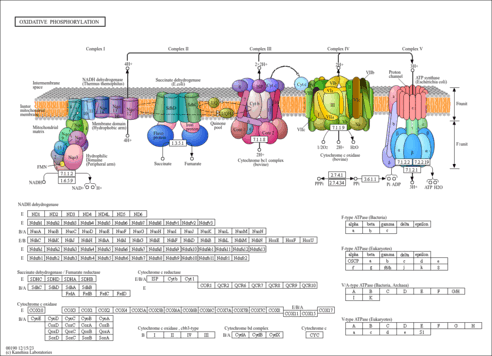
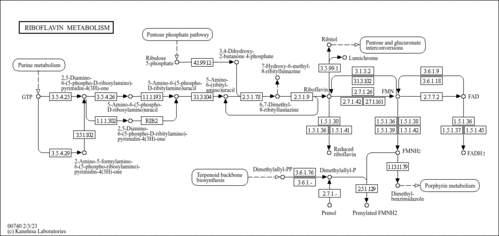
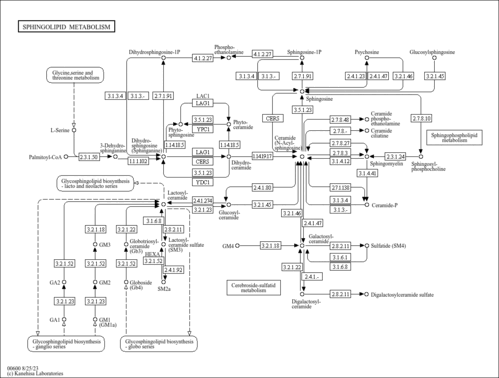
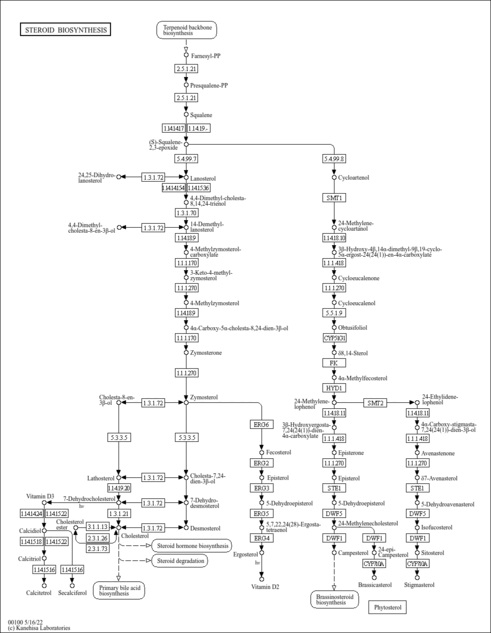
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Wynn, Richard L. Production of hydrogen and oxygen by thermal disassociation of water. U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ. (2007), 26pp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in D-arabinono-1,4-lactone oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Can oxidize L-gulono-1,4-lactone as well as D-arabinono- 1,4-lactone and L-galactono-1,4-lactone
- Gene Name:
- ALO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P54783
- Molecular weight:
- 59493.19922
Reactions
| D-arabinono-1,4-lactone + O(2) → dehydro-D-arabinono-1,4-lactone + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes C14-demethylation of lanosterol which is critical for ergosterol biosynthesis. It transforms lanosterol into 4,4'-dimethyl cholesta-8,14,24-triene-3-beta-ol
- Gene Name:
- ERG11
- Uniprot ID:
- P10614
- Molecular weight:
- 60719.80078
Reactions
| Obtusifoliol + 3 O(2) + 3 NADPH → 4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-ergosta-8,14,24(28)-trien-3-beta-ol + formate + 3 NADP(+) + 4 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxamine-phosphate oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of either pyridoxine 5'- phosphate (PNP) or pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP) into pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)
- Gene Name:
- PDX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38075
- Molecular weight:
- 26908.0
Reactions
| Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate + H(2)O + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
| Pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the production of beta-alanine, a precursor of pantothenic acid. Multicopy suppressor of fenpropimorph resistance
- Gene Name:
- FMS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P50264
- Molecular weight:
- 57805.10156
Reactions
| Spermine + O(2) + H(2)O → spermidine + 3-aminopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| Spermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → putrescine + 3-aminopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(1)-acetylspermine + O(2) + H(2)O → spermidine + 3-acetamidopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(1)-acetylspermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → putrescine + 3-acetamidopropanal + H(2)O(2). |
| N(8)-acetylspermidine + O(2) + H(2)O → 4-acetamidobutanal + trimethylenediamine + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-CoA + O(2) = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2)
- Gene Name:
- POX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13711
- Molecular weight:
- 84041.39844
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + O(2) → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid elongase activity
- Specific function:
- May be a membrane bound enzyme involved in the highly specific elongation of saturated 14-carbon fatty acids (14:0) to 16-carbon species (16:0)
- Gene Name:
- ELO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P39540
- Molecular weight:
- 36233.60156
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA → 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Carrier of the growing fatty acid chain in fatty acid biosynthesis. May be involved in the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids. Accessory and non-catalytic subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), which functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain
- Gene Name:
- ACP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32463
- Molecular weight:
- 13942.5
- General function:
- Involved in oxygen-dependent protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen-IX to form protoporphyrin-IX
- Gene Name:
- HEM14
- Uniprot ID:
- P40012
- Molecular weight:
- 59702.39844
Reactions
| Protoporphyrinogen-IX + 3 O(2) → protoporphyrin-IX + 3 H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in heme biosynthesis. Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of propionic acid side chains of rings A and B of coproporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- HEM13
- Uniprot ID:
- P11353
- Molecular weight:
- 37711.30078
Reactions
| Coproporphyrinogen-III + O(2) + 2 H(+) → protoporphyrinogen-IX + 2 CO(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Could be a fumarate reductase
- Gene Name:
- OSM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21375
- Molecular weight:
- 55064.80078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in monooxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) to form 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine (L-3OHKyn). Required for synthesis of quinolinic acid
- Gene Name:
- BNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P38169
- Molecular weight:
- 52428.89844
Reactions
| L-kynurenine + NADPH + O(2) → 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine + NADP(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The outer membrane form may mediate the reduction of outer membrane cytochrome b5, and the soluble inter-membrane space form may transfer electrons from external NADH to cytochrome c, thereby mediating an antimycin-insensitive, energy-coupled oxidation of external NADH by yeast mitochondria. Involved in the reduction of D-erythroascorbyl free radicals
- Gene Name:
- MCR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36060
- Molecular weight:
- 34137.69922
Reactions
| NADH + 2 ferricytochrome b5 → NAD(+) + H(+) + 2 ferrocytochrome b5. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts as a alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase active on sulfonates. Although taurine is a poor substrate, a variety of other sulfonates are utilized, with the best natural substrates being isethionate and taurocholate
- Gene Name:
- JLP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12358
- Molecular weight:
- 46982.30078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Required for biosynthesis of nicotinic acid
- Gene Name:
- BNA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P47125
- Molecular weight:
- 50774.80078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in protein complex assembly
- Specific function:
- Required for the assembly of yeast cytochrome oxidase. Involved in the biosynthesis of heme A and the initial step in this pathway, the hydroxylation of heme O, is thought to be catalyzed by a three-component mono-oxygenase consisting of COX15, ferredoxin and ferredoxin reductase
- Gene Name:
- COX15
- Uniprot ID:
- P40086
- Molecular weight:
- 54657.89844
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is suggested to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway
- Gene Name:
- ERG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32476
- Molecular weight:
- 55125.39844
Reactions
| Squalene + AH(2) + O(2) → (S)-squalene-2,3-epoxide + A + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in ubiquinone biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Component of the coenzyme Q biosynthetic pathway. May play a role in organizing a multi-subunit COQ enzyme complex required for coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Required for steady-state levels of COQ3, COQ4, COQ6, COQ7 and COQ9 polypeptides
- Gene Name:
- COQ4
- Uniprot ID:
- O13525
- Molecular weight:
- 38626.80078
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the first step in the removal of the two C-4 methyl groups of 4,4-dimethylzymosterol
- Gene Name:
- ERG25
- Uniprot ID:
- P53045
- Molecular weight:
- 36478.89844
Reactions
| 4,4-dimethyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
| 4-beta-hydroxymethyl-4-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-en-3-beta-ol + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O. |
| 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carbaldehyde + NAD(P)H + O(2) → 3-beta-hydroxy-4-beta-methyl-5-alpha-cholest-7-ene-4-alpha-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in ferroxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Promotes the biosynthesis of heme as well as the assembly and repair of iron-sulfur clusters by delivering Fe(2+) to proteins involved in these pathways. Plays a role in the protection against iron-catalyzed oxidative stress through its ability to catalyze the oxidation of Fe(2+) to Fe(3+). Can store large amounts of the metal in the form of a ferrihydrite mineral by oligomerization. May be involved in regulation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain
- Gene Name:
- YFH1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07540
- Molecular weight:
- 19490.0
Reactions
| 4 Fe(2+) + 4 H(+) + O(2) → 4 Fe(3+) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative ring opening of 3- hydroxyanthranilate to 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde, which spontaneously cyclizes to quinolinate
- Gene Name:
- BNA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P47096
- Molecular weight:
- 20234.90039
Reactions
| 3-hydroxyanthranilate + O(2) → 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Required for hydroxylation of C-4 in the sphingoid moiety of ceramide. Involved in the response to syringomycin
- Gene Name:
- SUR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P38992
- Molecular weight:
- 40734.0
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- SOD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00445
- Molecular weight:
- 15854.59961
Reactions
| 2 superoxide + 2 H(+) → O(2) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in superoxide dismutase activity
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- SOD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P00447
- Molecular weight:
- 25774.09961
Reactions
| 2 superoxide + 2 H(+) → O(2) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- In the de novo pyrimidine biosynthesic pathway, catalyzes the stereospecific oxidation of (S)-dihydroorotate to orotate and the reduction of fumarate to succinate. Does not use oxaloacetate and NAD or NADP as electron acceptors
- Gene Name:
- URA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P28272
- Molecular weight:
- 34800.60156
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + O(2) → orotate + H(2)O(2). |
| (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone → orotate + a quinol |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme is required for electron transfer from NADP to cytochrome P450 in microsomes. It can also provide electron transfer to heme oxygenase and cytochrome B5
- Gene Name:
- NCP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16603
- Molecular weight:
- 76771.10156
Reactions
| NADPH + n oxidized hemoprotein → NADP(+) + n reduced hemoprotein. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain
- Gene Name:
- CYC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00044
- Molecular weight:
- 12181.90039
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain
- Gene Name:
- CYC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P00045
- Molecular weight:
- 12532.2998
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilizes O(2) and electrons from the reduced cytochrome b(5) domain to catalyze the insertion of a double bond into a spectrum of fatty acyl-CoA substrates (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- OLE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21147
- Molecular weight:
- 58402.60156
Reactions
| Stearoyl-CoA + 2 ferrocytochrome b5 + O(2) + 2 H(+) → oleoyl-CoA + 2 ferricytochrome b5 + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Ceramide hydroxylase involved in the alpha-hydroxylation of sphingolipid-associated very long chain fatty acids. Hydroxylates the very long chain fatty acid of ceramides at C2 and C3
- Gene Name:
- SCS7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03529
- Molecular weight:
- 44881.10156
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the introduction of a C-5 double bond in the B ring of ergosterol. May contribute to the regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- ERG3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32353
- Molecular weight:
- 42729.89844
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide
- Gene Name:
- CTT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06115
- Molecular weight:
- 64583.0
Reactions
| 2 H(2)O(2) → O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide
- Gene Name:
- CTA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15202
- Molecular weight:
- 58555.19922
Reactions
| 2 H(2)O(2) → O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- FAD-dependent sulfhydryl oxidase that catalyzes disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen in parallel to ERO1
- Gene Name:
- ERV2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12284
- Molecular weight:
- 22141.30078
Reactions
| 4 R'C(R)SH + O(2) → 2 R'C(R)S-S(R)CR' + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- FAD-dependent sulfhydryl oxidase that catalyzes disulfide bond formation. Required for the import and folding of small cysteine-containing proteins in the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS). Forms a redox cycle with MIA40 that involves a disulfide relay system. Important for maintaining the cysteine residues in MIA40 in an oxidized state. Reduced ERV1 is reoxidized by cytochrome c. Required for the maturation of cytoplasmic, but not of mitochondrial Fe/S proteins
- Gene Name:
- ERV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P27882
- Molecular weight:
- 21639.30078
Reactions
| 4 R'C(R)SH + O(2) → 2 R'C(R)S-S(R)CR' + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Electron donor reductase for cytochrome b5. The cytochrome b5/NADH cytochrome b5 reductase electron transfer system supports the catalytic activity of several sterol biosynthetic enzymes. Plays a role in bud morphology
- Gene Name:
- CBR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38626
- Molecular weight:
- 31493.59961
Reactions
| NADH + 2 ferricytochrome b5 → NAD(+) + H(+) + 2 ferrocytochrome b5. |