| Identification |
|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00700 |
|---|
| Name | dATP |
|---|
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|
| Strain | Baker's yeast |
|---|
| Description | Deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) is a nucleotide used in cells for DNA synthesis. DNA usually exists as a double-stranded structure, with both strands coiled together to form the characteristic double-helix. Each single strand of DNA is a chain of four types of nucleotides having the bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. A nucleotide is a mono-, di-, or triphosphate deoxyribonucleoside; that is, a deoxyribose sugar is attached to one, two, or three phosphates. Chemical interaction of these nucleotides forms phosphodiester linkages, creating the phosphate-deoxyribose backbone of the DNA double helix with the bases pointing inward. Nucleotides (bases) are matched between strands through hydrogen bonds to form base pairs. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | - 2-deoxyadenosine 5-triphosphate
- 2'-Deoxy-5'-ATP
- 2'-Deoxy-ATP
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphate
- 2'-deoxyadenosine triphosphate
- dATP
- Deoxy-ATP
- deoxyadenosine 5-triphosphate
- Deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphate
- deoxyadenosine triphosphate
- deoxyadenosine-triphosphate
- DTP
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphoric acid
- Deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphoric acid
- Deoxyadenosine triphosphoric acid
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine triphosphate, 14C-labeled
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine triphosphate, monomagnesium salt
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine triphosphate, trisodium salt
- 2'-Deoxyadenosine triphosphate, p'-(32)p-labeled
- dATP CPD
|
|---|
| CAS number | 1927-31-7 |
|---|
| Weight | Average: 491.1816
Monoisotopic: 491.000830537 |
|---|
| InChI Key | SUYVUBYJARFZHO-RRKCRQDMSA-N |
|---|
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H16N5O12P3/c11-9-8-10(13-3-12-9)15(4-14-8)7-1-5(16)6(25-7)2-24-29(20,21)27-30(22,23)26-28(17,18)19/h3-7,16H,1-2H2,(H,20,21)(H,22,23)(H2,11,12,13)(H2,17,18,19)/t5-,6+,7+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | ({[({[(2R,3S,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name | dATP |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H16N5O12P3 |
|---|
| SMILES | NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O)O1 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates. These are purine nucleotides with triphosphate group linked to the ribose moiety lacking a hydroxyl group at position 2. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
| Class | Purine nucleotides |
|---|
| Sub Class | Purine deoxyribonucleotides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
- 6-aminopurine
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Pyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- Alkyl phosphate
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Charge | 0 |
|---|
| Melting point | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Water Solubility | Not Available | PhysProp | | LogP | Not Available | PhysProp |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
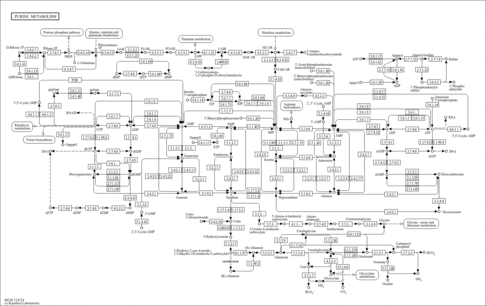
| SMPDB Pathways | | purine nucleotides de novo biosynthesis | PW002478 |    |
|
|---|
| KEGG Pathways | |
|---|
| SMPDB Reactions | |
|---|
| KEGG Reactions | |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Intracellular Concentrations | |
|---|
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-002e-9843300000-a8d959008963a6e8a26c | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-007p-9218120000-4918f13056a529d12752 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4r-1914800000-a1027d5e4feaa6e70b54 | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0100900000-53e4238ba311a2bd32bf | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a6r-5910000000-b8a47704262fccc007c0 | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-000f-0800900000-fa3d4e7a131ac1b4c8e7 | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-000i-1900000000-91f17c669f5b4e231613 | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-000i-2900000000-66cc97431dd4c6ef5edb | JSpectraViewer | MoNA | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0220900000-5fd893f07f0f264099fd | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-003r-5950100000-3901292643e421d47188 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-9200000000-c3a099b6927fdfbe3098 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0000900000-be4507fb31a2c98dc9ed | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0570-7900600000-3df5f7dd826575e2717f | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-9000000000-e1f5b79920ef4f1ff109 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0911200000-81436267b4eed8c39c3f | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-dad0a3294356131635d0 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000i-1900000000-a1b841f4410b13c0280f | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000l-0900500000-1ef5399a134e840e1033 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-3a76b30592d0f0552de6 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-001c-0921000000-b0230592c2387afe5f4d | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 2D NMR | [1H,13C] 2D NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer |
|
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Herrgard, M. J., Swainston, N., Dobson, P., Dunn, W. B., Arga, K. Y., Arvas, M., Bluthgen, N., Borger, S., Costenoble, R., Heinemann, M., Hucka, M., Le Novere, N., Li, P., Liebermeister, W., Mo, M. L., Oliveira, A. P., Petranovic, D., Pettifer, S., Simeonidis, E., Smallbone, K., Spasic, I., Weichart, D., Brent, R., Broomhead, D. S., Westerhoff, H. V., Kirdar, B., Penttila, M., Klipp, E., Palsson, B. O., Sauer, U., Oliver, S. G., Mendes, P., Nielsen, J., Kell, D. B. (2008). "A consensus yeast metabolic network reconstruction obtained from a community approach to systems biology." Nat Biotechnol 26:1155-1160.18846089
- Chabes, A., Stillman, B. (2007). "Constitutively high dNTP concentration inhibits cell cycle progression and the DNA damage checkpoint in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1183-1188.17227840
- Chabes, A., Georgieva, B., Domkin, V., Zhao, X., Rothstein, R., Thelander, L. (2003). "Survival of DNA damage in yeast directly depends on increased dNTP levels allowed by relaxed feedback inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase." Cell 112:391-401.12581528
- Prieto, S., Bouillaud, F., Rial, E. (1996). "The nature and regulation of the ATP-induced anion permeability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria." Arch Biochem Biophys 334:43-49.8837737
- Coda-Zabetta, F., Boam, D. S. (1996). "Distinct effects of ATP on transcription complex formation and initiation in a yeast in vitro transcription system." Biochim Biophys Acta 1306:194-202.8634337
- Muller, E. G. (1994). "Deoxyribonucleotides are maintained at normal levels in a yeast thioredoxin mutant defective in DNA synthesis." J Biol Chem 269:24466-24471.7929110
- Koc, A., Wheeler, L. J., Mathews, C. K., Merrill, G. F. (2004). "Hydroxyurea arrests DNA replication by a mechanism that preserves basal dNTP pools." J Biol Chem 279:223-230.14573610
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|