| Identification |
|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00301 |
|---|
| Name | Palmityl-CoA |
|---|
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|
| Strain | Baker's yeast |
|---|
| Description | Palmityl-CoA, also known as palmitoyl CoA or CoA, palmitoyl, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as long-chain fatty acyl coas. These are acyl CoAs where the group acylated to the coenzyme A moiety is a long aliphatic chain of 13 to 21 carbon atoms. Palmityl-CoA is a strong basic compound (based on its pKa). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | - hexadecanoyl CoA
- hexadecanoyl Coenzyme A
- palmitoyl CoA
- palmitoyl coenzyme a
- palmitoyl-CoA
- palmitoyl-Coenzyme A
- Palmityl-CoA
- Palmityl-Coenzyme A
- s-hexadecanoate
- s-hexadecanoate CoA
- s-hexadecanoate Coenzyme A
- s-hexadecanoic acid
- s-palmitoylcoenzyme a
- CoA, Palmitoyl
- CoA, Hexadecanoyl
- coenzyme A, Palmitoyl
- Palmityl CoA
- CoA, Palmityl
|
|---|
| CAS number | 1763-10-6 |
|---|
| Weight | Average: 1005.943
Monoisotopic: 1005.344873947 |
|---|
| InChI Key | MNBKLUUYKPBKDU-TZIIWEFPSA-N |
|---|
| InChI | InChI=1S/C37H66N7O17P3S/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-28(46)65-21-20-39-27(45)18-19-40-35(49)32(48)37(2,3)23-58-64(55,56)61-63(53,54)57-22-26-31(60-62(50,51)52)30(47)36(59-26)44-25-43-29-33(38)41-24-42-34(29)44/h24-26,30-32,36,47-48H,4-23H2,1-3H3,(H,39,45)(H,40,49)(H,53,54)(H,55,56)(H2,38,41,42)(H2,50,51,52)/t26-,30-,31-,32?,36-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-2-[({[({3-[(2-{[2-(hexadecanoylsulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)methyl]-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2-{[({3-[(2-{[2-(hexadecanoylsulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]methyl}-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl]oxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C37H66N7O17P3S |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]OC([H])(C(=O)N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])SC(=O)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])OP(=O)(O[H])OP(=O)(O[H])OC([H])([H])[C@@]1([H])O[C@@]([H])(N2C([H])=NC3=C2N=C([H])N=C3N([H])[H])[C@]([H])(O[H])[C@]1([H])OP(=O)(O[H])O[H] |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as long-chain fatty acyl coas. These are acyl CoAs where the group acylated to the coenzyme A moiety is a long aliphatic chain of 13 to 21 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Long-chain fatty acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Monosaccharide
- Pyrimidine
- Alkyl phosphate
- Fatty amide
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Sulfenyl compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organosulfur compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Amine
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Charge | 0 |
|---|
| Melting point | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Water Solubility | Not Available | PhysProp | | LogP | Not Available | PhysProp |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - lipid particle
- endoplasmic reticulum
- peroxisome
- vacuole
- cytoplasm
|
|---|
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | PW002403 |    | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids (docosanoyl) | PW002408 |    | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids (icosanoyl) | PW002434 |    | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids (stearoyl) | PW002435 |    | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids (tetracosanoyl-CoA) | PW002404 |    |
|
|---|
| KEGG Pathways | | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ec01040 | 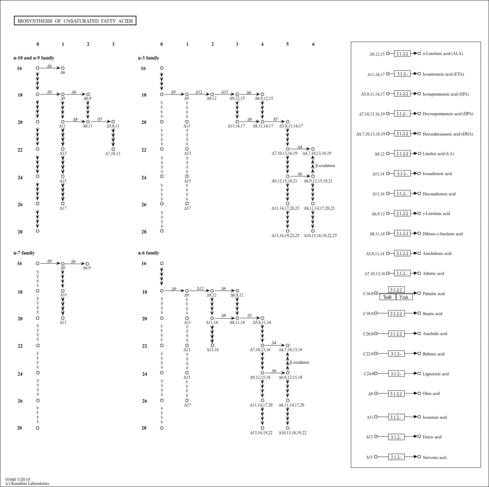 | | Fatty acid elongation in mitochondria | ec00062 | 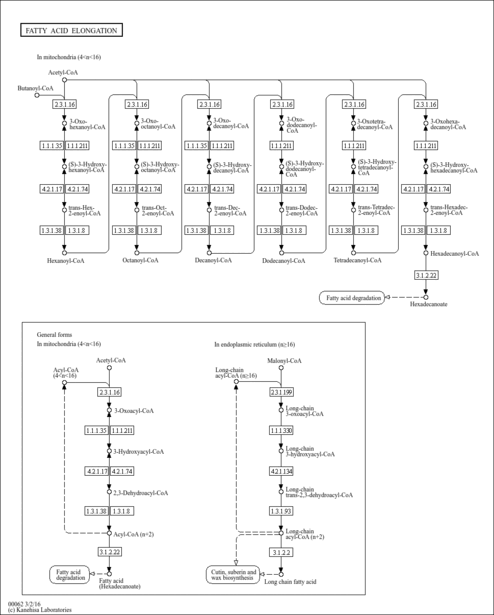 | | Fatty acid metabolism | ec00071 | 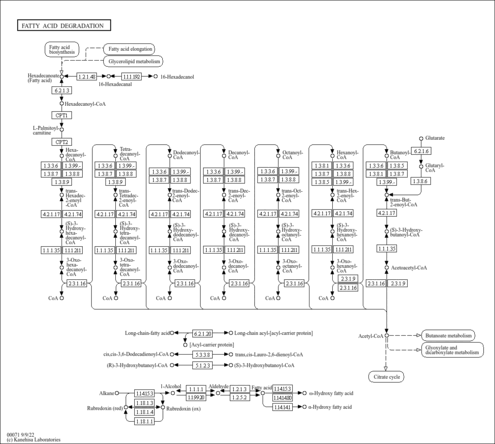 | | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | ec00564 | 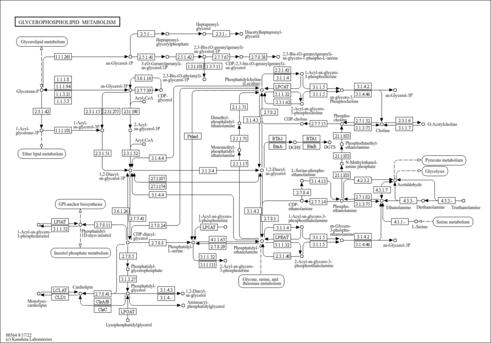 | | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | ec00563 |  |
|
|---|
| SMPDB Reactions |
|
|---|
| KEGG Reactions |
|
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - UniProt Consortium (2011). "Ongoing and future developments at the Universal Protein Resource." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D214-D219.21051339
- Dickson, R. C., Sumanasekera, C., Lester, R. L. (2006). "Functions and metabolism of sphingolipids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae." Prog Lipid Res 45:447-465.16730802
- Cowart, L. A., Hannun, Y. A. (2005). "Using genomic and lipidomic strategies to investigate sphingolipid function in the yeast heat-stress response." Biochem Soc Trans 33:1166-1169.16246073
- Obeid, L. M., Okamoto, Y., Mao, C. (2002). "Yeast sphingolipids: metabolism and biology." Biochim Biophys Acta 1585:163-171.12531550
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|





