| Identification |
|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00880 |
|---|
| Name | S-D-Lactoylglutathione |
|---|
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|
| Strain | Baker's yeast |
|---|
| Description | S-Lactoylglutathione is the product of reacting methylglyoxal with glutathione by the enzyme Glyoxalase I. The enzyme Glyoxalase II converts S-Lactoylglutathione into d-latic acid and glutathione. Methylglyoxal a glycolysis product that is toxic due to its high reactivity and thus the the glyoxalase system, made up of Glyoxalase I and Glyoxalase II is important in metabolising it. [PMID: 21310260] |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | - (4-Carboxyphenyl)chloromercury
- (R)-S-lactoylglutathione
- 4-Carboxyphenylmercuric chloride
- 4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid
- Benzoic acid, p-(chloromercuri)
- D-lactoylglutathione
- delta-lactoylglutathione
- Mercurate(1-), (4-carboxylatophenyl)chloro-, hydrogen
- Mercury, (4-carboxyphenyl)chloro-
- Mercury, (p-carboxyphenyl)chloro-
- p-(Chloromercuri)benzoic acid
- p-Carboxyphenylmercuric chloride
- p-Chlormercuribenzoic acid
- p-Chloromercuric benzoic acid
- p-Chloromercurybenzoic acid
- PCMB
- S-D-lactoyl-glutathione
- S-delta-lactoyl-glutathione
- S-delta-lactoylglutathione
- S-lactate glutathione
- S-lactateglutathione
- S-lactoyl-glutathione
- S-lactylglutathione
- Usaf d-3
- S-D-Lactoylglutathione
- 2-amino-3-({[(2R)-2-hydroxypropanoyl]sulfanyl}methyl)butanedioate
- 2-amino-3-({[(2R)-2-hydroxypropanoyl]sulphanyl}methyl)butanedioate
- 2-amino-3-({[(2R)-2-hydroxypropanoyl]sulphanyl}methyl)butanedioic acid
|
|---|
| CAS number | 59-85-8 |
|---|
| Weight | Average: 251.257
Monoisotopic: 251.046357843 |
|---|
| InChI Key | DWPTUFGRYYIXHG-JYMNUSQCSA-N |
|---|
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H13NO6S/c1-3(10)8(15)16-2-4(6(11)12)5(9)7(13)14/h3-5,10H,2,9H2,1H3,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)/t3-,4?,5?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-amino-3-({[(2R)-2-hydroxypropanoyl]sulfanyl}methyl)butanedioic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name | 2-amino-3-({[(2R)-2-hydroxypropanoyl]sulfanyl}methyl)butanedioic acid |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H13NO6S |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@](C)(O)C(=O)SCC(C(N)C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid
- Branched fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Thia fatty acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Sulfenyl compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Charge | 0 |
|---|
| Melting point | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Water Solubility | Not Available | PhysProp | | LogP | Not Available | PhysProp |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways | |
|---|
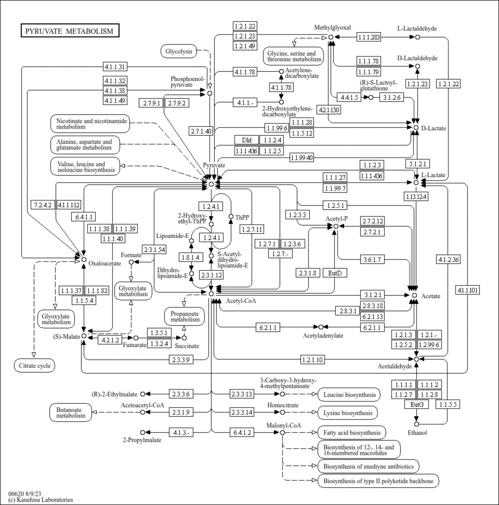
| KEGG Pathways | |
|---|
| SMPDB Reactions | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG Reactions | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00dm-9310000000-d9aec94e9f3538320b5d | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0pc0-0970000000-d2c2a69bd5d6f6a4ff5e | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fr-7930000000-ae9d21e38c3e84bfac90 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0ue9-1900000000-cf37b4735e36252013c4 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-1930000000-896585d5b044aa8ee7e3 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03l0-2920000000-0d461f8185f193493814 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-9300000000-85e14c7d7cc91df2f5e6 | JSpectraViewer |
|
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Scheer, M., Grote, A., Chang, A., Schomburg, I., Munaretto, C., Rother, M., Sohngen, C., Stelzer, M., Thiele, J., Schomburg, D. (2011). "BRENDA, the enzyme information system in 2011." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D670-D676.21062828
- Martins, A. M., Mendes, P., Cordeiro, C., Freire, A. P. (2001). "In situ kinetic analysis of glyoxalase I and glyoxalase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae." Eur J Biochem 268:3930-3936.11453985
- Inoue, Y., Maeta, K., Nomura, W. (2011). "Glyoxalase system in yeasts: structure, function, and physiology." Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:278-284.21310260
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|