| Identification |
|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00177 |
|---|
| Name | (S)-2-Acetolactate |
|---|
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|
| Strain | Baker's yeast |
|---|
| Description | (S)-2-Acetolactate, also known as b-dyn a, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain keto acids and derivatives. These are keto acids with an alkyl chain the contains less than 6 carbon atoms (S)-2-Acetolactate is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral (S)-2-Acetolactate exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within yeast, (S)-2-acetolactate participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, (S)-2-acetolactate can be biosynthesized from pyruvic acid through its interaction with the enzyme acetolactate synthase / acetohydroxybutanoate synthase. In addition, (S)-2-acetolactate can be biosynthesized from pyruvic acid through its interaction with the enzyme acetohydroxybutanoate synthase / acetolactate synthase. In yeast, (S)-2-acetolactate is involved in the metabolic pathway called valine biosynthesis pathway. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | - (S)-2-Hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate
- (S)-2-Hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid
- (2S)-2-Hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate
- (2S)-2-Hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid
- (S)-2-Acetolactic acid
- 13-Biotinyl-lys-dynorphin a amide (1-13)
- b-DYN a
- (S)-alpha-Acetolactic acid
- (S)-α-Acetolactic acid
- 2-Acetolactic acid
- 2-Hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid
- Acetolactic acid
|
|---|
| CAS number | Not Available |
|---|
| Weight | Average: 132.1146
Monoisotopic: 132.042258744 |
|---|
| InChI Key | NMDWGEGFJUBKLB-YFKPBYRVSA-N |
|---|
| InChI | InChI=1S/C5H8O4/c1-3(6)5(2,9)4(7)8/h9H,1-2H3,(H,7,8)/t5-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name | acetolactic acid |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C5H8O4 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]OC(=O)[C@@](O[H])(C(=O)C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain keto acids and derivatives. These are keto acids with an alkyl chain the contains less than 6 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Beta-keto acid
- Branched fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Short-chain keto acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Alpha-hydroxy acid
- Fatty acyl
- Acyloin
- Beta-hydroxy ketone
- Hydroxy acid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Alpha-hydroxy ketone
- Ketone
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Charge | 0 |
|---|
| Melting point | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Water Solubility | Not Available | PhysProp | | LogP | Not Available | PhysProp |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Organoleptic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways | |
|---|
| KEGG Pathways | | Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis | ec00290 | 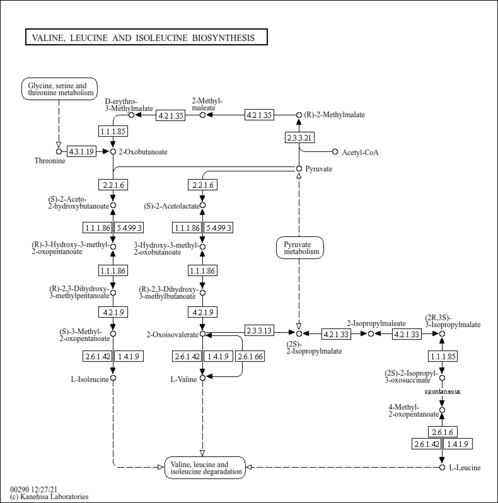 |
|
|---|
| SMPDB Reactions | |
|---|
| KEGG Reactions | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-0c1fe460a2ec8a1a255d | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0303-9780000000-ed6c7b366835f2a4a9c0 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-001i-5900000000-a14af8bd96fdcce5e84f | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-015l-9400000000-53c1f10a4a9b63a25574 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-01b9-9000000000-03c96ef4ce31ab174fdd | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0019-9700000000-641c507686f1b0493bde | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000i-9000000000-cd68c82882667330e329 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0079-9000000000-f0530bd3c4f32baa697c | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-9300000000-0c998add67e750d36bc4 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000i-9200000000-3e8a380405cb5b02d1d7 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-aeeb164d9240ff735bc5 | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00ke-9200000000-c8b983df55a14da2898a | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-79267be0bc618dc8018f | JSpectraViewer | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-cd1679ff8fbd31e9b90f | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | JSpectraViewer |
|
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - UniProt Consortium (2011). "Ongoing and future developments at the Universal Protein Resource." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D214-D219.21051339
- Scheer, M., Grote, A., Chang, A., Schomburg, I., Munaretto, C., Rother, M., Sohngen, C., Stelzer, M., Thiele, J., Schomburg, D. (2011). "BRENDA, the enzyme information system in 2011." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D670-D676.21062828
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|

