Ammonia (YMDB00091)
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB00091 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Ammonia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strain | Baker's yeast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Ammonia, also known as NH3 or amoniaco, belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. Ammonia is a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). Ammonia exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Ammonia is a potentially toxic compound. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | 7664-41-7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | Average: 17.0305 Monoisotopic: 17.026549101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI | InChI=1S/H3N/h1H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | ammonia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name | ammonia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | H3N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H]N([H])[H] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | -77.7 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organoleptic Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
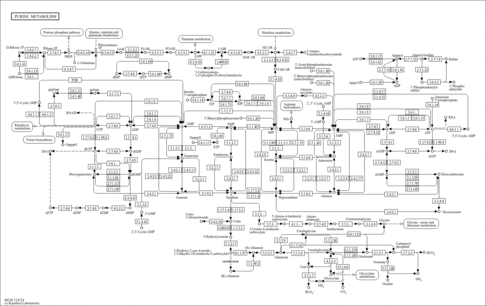
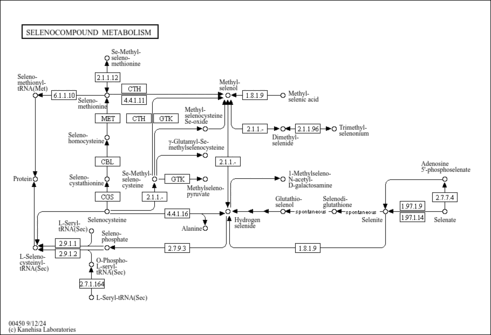
| KEGG Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Reactions | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular Concentrations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Mohr, Rudolf. Ammonia separation from offgas obtained from melamine synthesis. U.S. (1971), 5 pp. CODEN: USXXAM US 3555784 19710119 CAN 77:50902 AN 1972:450902 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen
- Gene Name:
- URA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P28274
- Molecular weight:
- 64709.80078
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine
- Gene Name:
- GLN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32288
- Molecular weight:
- 41705.60156
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen. Plays an important role in the regulation of phospholipid synthesis
- Gene Name:
- URA8
- Uniprot ID:
- P38627
- Molecular weight:
- 63055.69922
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) → ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- Hydrolysis of urea to ammonia and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- DUR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P32528
- Molecular weight:
- 201830.0
Reactions
| ATP + urea + HCO(3)(-) → ADP + phosphate + urea-1-carboxylate. |
| Urea-1-carboxylate + H(2)O → 2 CO(2) + 2 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in ureidoglycolate hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Utilization of purines as secondary nitrogen sources, when primary sources are limiting
- Gene Name:
- DAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32459
- Molecular weight:
- 21726.59961
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + H(2)O → glyoxylate + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxamine-phosphate oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of either pyridoxine 5'- phosphate (PNP) or pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP) into pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)
- Gene Name:
- PDX3
- Uniprot ID:
- P38075
- Molecular weight:
- 26908.0
Reactions
| Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate + H(2)O + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
| Pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + O(2) → pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate
- Gene Name:
- CYS3
- Uniprot ID:
- P31373
- Molecular weight:
- 42541.69922
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-cysteine + NH(3) + 2-oxobutanoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- This enzyme scavenge exogenous and endogenous cytidine and 2'-deoxycytidine for UMP synthesis
- Gene Name:
- CDD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06549
- Molecular weight:
- 15535.90039
Reactions
| Cytidine + H(2)O → uridine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- AAH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53909
- Molecular weight:
- 39634.69922
Reactions
| Adenosine + H(2)O → inosine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-threonine = 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ILV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P00927
- Molecular weight:
- 63830.69922
Reactions
| L-threonine → 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- CHA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P25379
- Molecular weight:
- 39301.0
Reactions
| L-serine → pyruvate + NH(3). |
| L-threonine → 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Could be a fumarate reductase
- Gene Name:
- OSM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21375
- Molecular weight:
- 55064.80078
Reactions
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts cytosine to uracil or 5-methylcytosine to thymine by deaminating carbon number 4
- Gene Name:
- FCY1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12178
- Molecular weight:
- 17506.90039
Reactions
| Cytosine + H(2)O → uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the deamidation of nicotinamide, an early step in the NAD(+) salvage pathway. Positively regulates SIR2-mediated silencing and longevity by preventing the accumulation of intracellular nicotinamide, an inhibitor of SIR2, during times of stress. Acts also on nicotinyl hydroxamate
- Gene Name:
- PNC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53184
- Molecular weight:
- 24993.19922
Reactions
| Nicotinamide + H(2)O → nicotinate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- GDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P33327
- Molecular weight:
- 124331.0
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NAD(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP3-1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11163
- Molecular weight:
- 38686.19922
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH3
- Uniprot ID:
- P39708
- Molecular weight:
- 49626.80078
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethylbilane synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Tetrapolymerization of the monopyrrole PBG into the hydroxymethylbilane pre-uroporphyrinogen in several discrete steps
- Gene Name:
- HEM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28789
- Molecular weight:
- 36674.19922
Reactions
| 4 porphobilinogen + H(2)O → hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system (glycine decarboxylase complex) catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- GCV1
- Uniprot ID:
- P48015
- Molecular weight:
- 44468.69922
Reactions
| [Protein]-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + tetrahydrofolate → [protein]-dihydrolipoyllysine + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ASP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P38986
- Molecular weight:
- 41394.80078
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O → L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- GDH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P07262
- Molecular weight:
- 49569.60156
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) → 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Exhibits dehydratase activity specific for L-threo-3- hydroxyaspartate
- Gene Name:
- SRY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P36007
- Molecular weight:
- 34898.69922
Reactions
| Threo-3-hydroxy-L-aspartate → oxaloacetate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- SDL1
- Uniprot ID:
- P0CF21
- Molecular weight:
- 13942.90039
Reactions
| L-serine → pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- STR3
- Uniprot ID:
- P53101
- Molecular weight:
- 51828.0
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- AMP deaminase plays a critical role in energy metabolism
- Gene Name:
- AMD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15274
- Molecular weight:
- 93300.79688
Reactions
| AMP + H(2)O → IMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in riboflavin biosynthesis. Converts 2,5- diamino-6-(ribosylamino)-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate into 5- amino-6-(ribosylamino)-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione 5'-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- RIB2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12362
- Molecular weight:
- 67035.29688
Reactions
| tRNA uridine → tRNA pseudouridine. |
| 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine + H(2)O → 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- IRC7
- Uniprot ID:
- P43623
- Molecular weight:
- 36971.10156
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O → L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Supplies the nucleotide substrate for thymidylate synthetase
- Gene Name:
- DCD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P06773
- Molecular weight:
- 35645.69922
Reactions
| dCMP + H(2)O → dUMP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor
- Specific function:
- A monocarboxylic acid amide + H(2)O = a monocarboxylate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- AMD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P22580
- Molecular weight:
- 61409.5
Reactions
| A monocarboxylic acid amide + H(2)O → a monocarboxylate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of guanine, producing xanthine and ammonia
- Gene Name:
- GUD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07729
- Molecular weight:
- 55203.19922
Reactions
| Guanine + H(2)O → xanthine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in fumarate hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- FUM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08417
- Molecular weight:
- 53151.5
Reactions
| (S)-malate → fumarate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in D-serine ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts specifically D-serine to pyruvate and ammonia. May play a role in D-serine detoxification
- Gene Name:
- DSD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P53095
- Molecular weight:
- 47827.39844
Reactions
| D-serine → pyruvate + NH(3). |